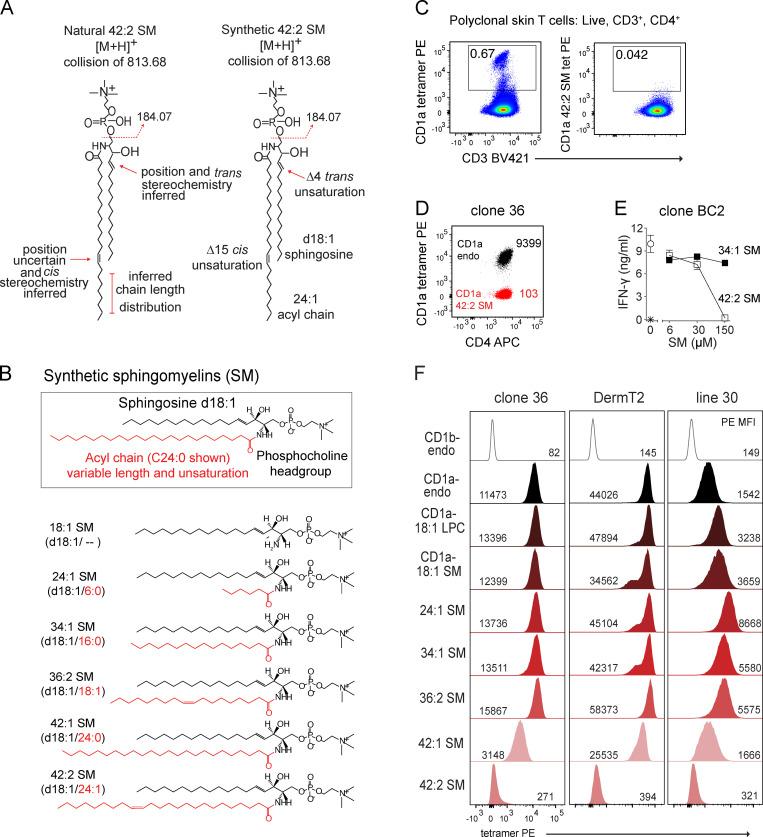
Figure 2.
Lipid chain length and unsaturation determine CD1a tetramer binding. (A) CD1a-eluted natural versus synthetic 42:2 SMs are shown with regard to known or inferred aspects of structure. (B) Synthetic SM variants differ in the length and saturation of the fatty acyl unit (red). (C) Polyclonal skin T cells stained with CD1a tetramer (tet) or tetramer treated with 42:2 SM, showing results that are representative of two experiments. (D) CD1a autoreactive skin T cell clone 36 staining with CD1a-endo or CD1a–42:2 SM, with results shown being representative of three experiments. Insets indicate tetramer MFI. (E) IFN-γ ELISA of clone BC2 T cells (star indicates T cells only) exposed to plate-bound CD1a treated with the synthetic SM, with results representative of two experiments. (F) CD1a–SM tetramer staining of skin T cell lines DermT2, Line 30, and Line 36. Cells were pregated (live, CD3+, CD4+ Autofluoresence[FITC]neg), and histograms were normalized to mode. [M+H], mass of the molecular ion plus a proton adduct.