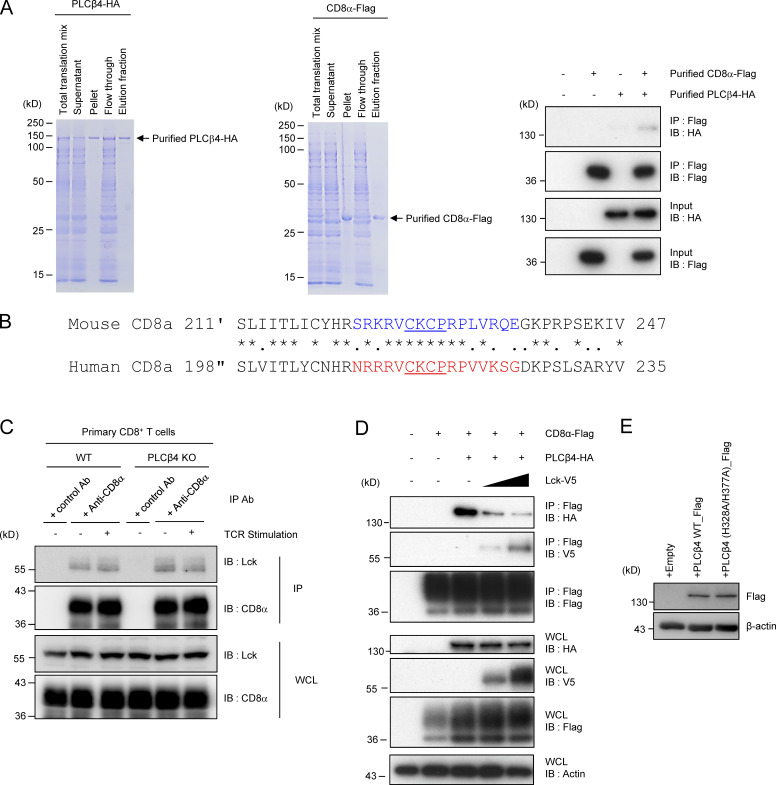
Figure S4.
Assessment of possible competition between PLCβ4 and Lck in their interaction with CD8α. (A) Coomassie blue staining of the purified His-tagged recombinant PLCβ4-HA (left) and CD8α-Flag protein. The PLCβ4-HA (100 ng) and/or CD8α-Flag (100 ng) proteins were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-Flag and detected by Western blot (IB) with the indicated Abs. (B) Comparison of amino acid sequences for cytoplasmic tails of mouse and human CD8α. Colored or underlined amino acids denote the PLCβ4 binding region or the zinc clasp structure, respectively. (C) Lysates of WT or PLCβ4-deficient primary CD8+ T cells unstimulated or stimulated with anti-CD3 (5 µg/ml)/anti-CD28 (2 µg/ml) for 30 min were immunoprecipitated with anti-CD8α and detected by Western blot with the indicated Abs. (D) Lysates of 293T cells transiently cotransfected with the indicated expression vectors were immunoprecipitated with anti-Flag and detected by Western blot with the indicated Abs. WCL, whole cell lysates. (E) Purified CD8+ T cells from PLCβ4-deficient mice were transduced with empty, PLCβ4 (WT), or a catalytically inactive mutant of PLCβ4 (H328A/H377A) construct. Protein levels of PLCβ4 (WT) and mutant of PLCβ4 (H328A/H377A) in the indicated lysates were determined by Western blotting with indicated Abs. Data are representative of two (E) or three (A, C, and D) independent experiments.