FIGURE 1.
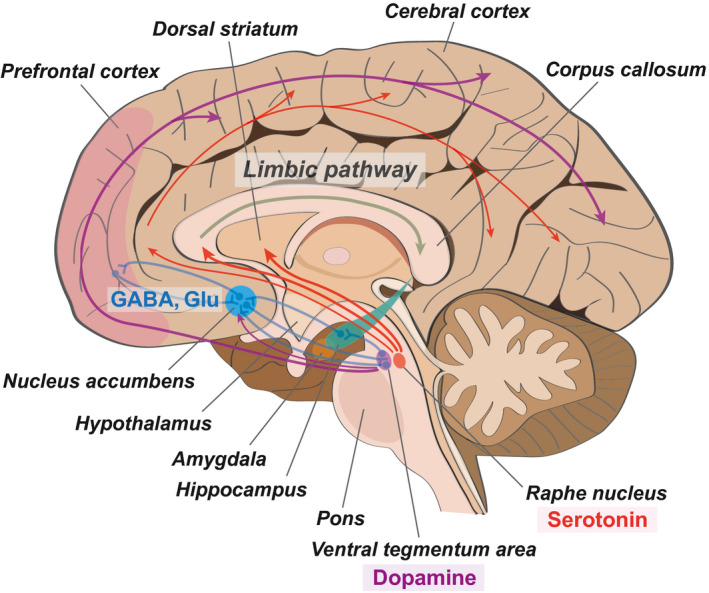
The neuroanatomical image of depression. This schematic image presents the important neurotransmitter pathway and the neuronal connection between different brain regions in depression. The nucleus accumbens plays as a critical connection hub in depression‐related brain regions. GABA (gamma‐aminobutyric acid) and Glu (glutamate), the neurotransmitters, contribute to the connective signal between the nucleus accumbens and the prefrontal cortex. Serotonin, which is secreted from the raphe nucleus of the brain stem, contributes to the limbic pathway and finally affects the hippocampus, related to cognitive function. Dopamine, another neurotransmitter, which is secreted from the ventral tegmentum area of the brain stem, influences the whole cerebral cortex region in the brain including the prefrontal cortex. See texts for the details. Red arrows indicate the serotonin pathway, and purple arrows indicate the dopamine pathway. Blue lines show the neuronal connection between different brain regions
