Figure 1. Analysis of Serum N-Acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectroscopy.
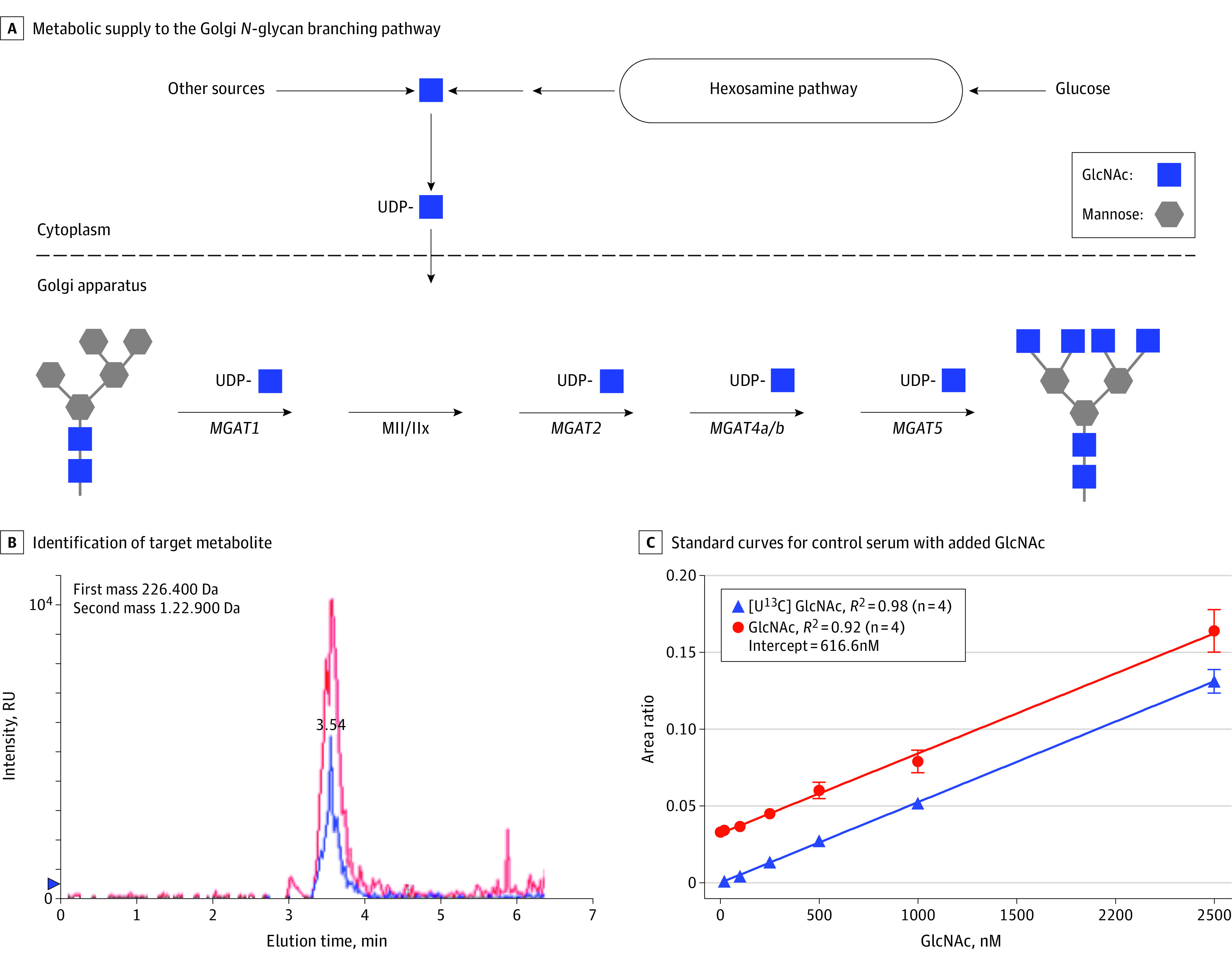
A, Schematic overview of metabolic supply to the Golgi N-glycan branching pathway. Uridine diphosphate (UDP)–GlcNAc, via de novo synthesis from glucose or salvage from GlcNAc, is the donor substrate used by the Mgat branching enzymes. B, The primary mass identifies the target metabolite, and the secondary or fragmented ion at time of liquid chromatography elution, as shown, is used to quantify N-acetylhexosamine (HexNAc). In the same run, endogenous serum HexNAc (red) and 500nM U13C-labeled GlcNAc standard (blue) are shown. The area under the peak for the fragmented ion is normalized to the internal standard, D7-glucose, added during sample preparation. C, Standard curves for control serum (39 individuals pooled) with either unlabeled GlcNAc or U13C-labeled GlcNAc at increasing concentrations added to the serum. The U13C-labeled GlcNAc shows measurement sensitivity to 20nM and confirms linearity to this concentration.
