Figure 4.
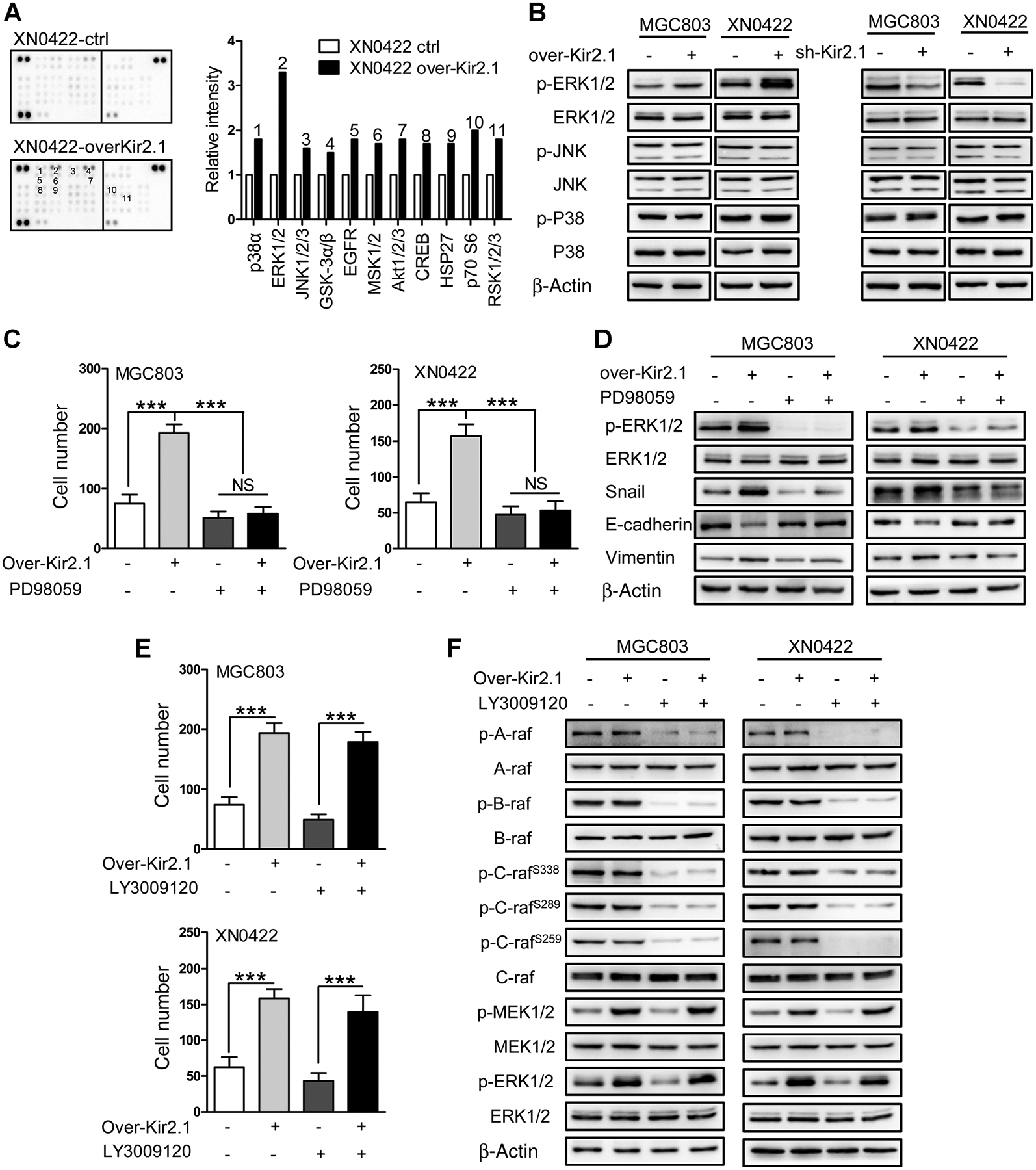
Kir2.1 activates MEK1/2–ERK1/2–Snail–EMT pathway independent of Raf. A, Human phosphokinase antibody array assay showing 11 elevated phosphorylation kinases (left) with ERK1/2 kinases at the highest level (right). Data are shown as mean. B, The over-Kir2.1 gastric cancer cells showing enhanced phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and sh-Kir2.1 gastric cancer cells showing attenuated phosphorylation of ERK1/2. JNK and p38, the other two members of MAPKs in gastric cancer cells, were unaffected by Kir2.1 expression status. C, Decreased invasion capability of gastric cancer cells after treatment with PD98059 (10 μmol/L), a MEK1/2-specific inhibitor. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 5; NS, not significant; ***, P < 0.0001, ANOVA test). D, Increased E-cadherin but decreased vimemtin, Snail, and pERK1/2 in PD98059 (10 μmol/L)-treated gastric cancer cells. E, Attenuation of the invasion capability of control gastric cancer cells by treatment with LY3009120 (20 μmol/L), a pan-Raf inhibitor, without effect on over-Kir2.1 gastric cancer cells. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 5; ***, P < 0.0001, Student t test). F, Attenuation of the level of pMEK1/2 and pERK1/2 in control gastric cancer cells by LY3009120 (20 μmol/L) treatment, without effect on over-Kir2.1 gastric cancer cells.
