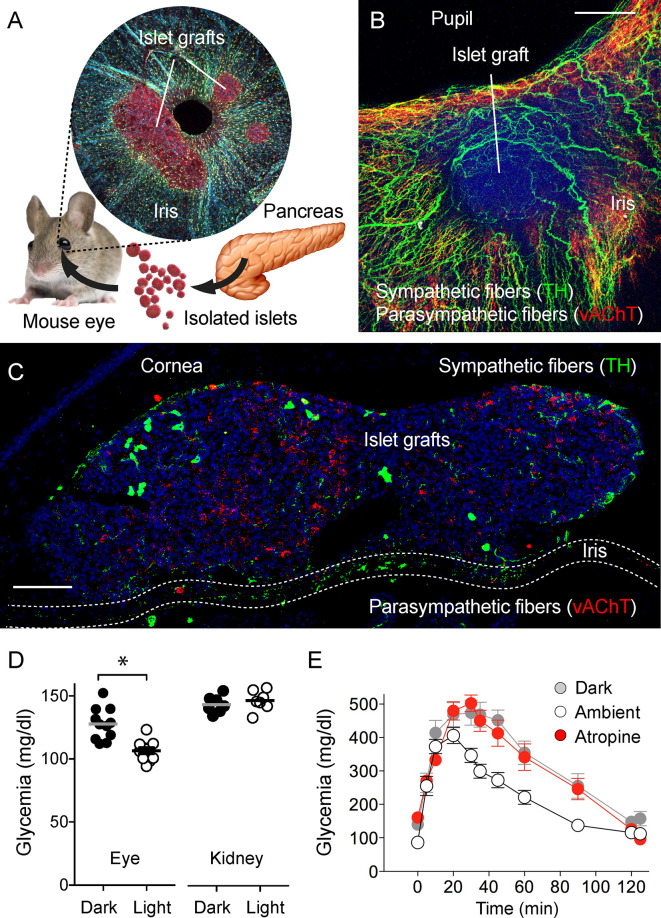
Figure 5.
Eye model for imaging innervation of pancreatic islet grafts [photomicrographs are from experiments conducted by Dr. Rayner Rodriguez-Diaz (A–C, unpublished data], data in (D) and (E) adapted and modified from Figure 4 in Rodriguez-Diaz et al., 2012). (A) Schematic representation of islet transplantation into the anterior chamber of the eye. Islets isolated from the pancreas are transplanted into the mouse eye. Microphotograph of an iris wholemount with islet grafts. (B) Z-stack of confocal images of a wholemount of the mouse iris with an islet graft immunostained for TH (green) and vAChT (red); scale bar 50 µm. (C) Confocal image of a cross-section of the mouse eye showing two islet grafts, stained for TH (green), vAChT (red), and DAPI (blue); scale bar 50 µm. (D) Plasma glucose levels in mice transplanted with islets in the anterior chamber of the eye or under the kidney capsule, in ambient light or in the dark (*p < 0.05, paired Student’s t-test). (E) Glucose excursion during an IPGTT of transplanted mice performed in the dark (gray symbols), ambient light (open symbols), or in ambient light after topical application of the muscarinic receptor antagonist atropine (red symbols).