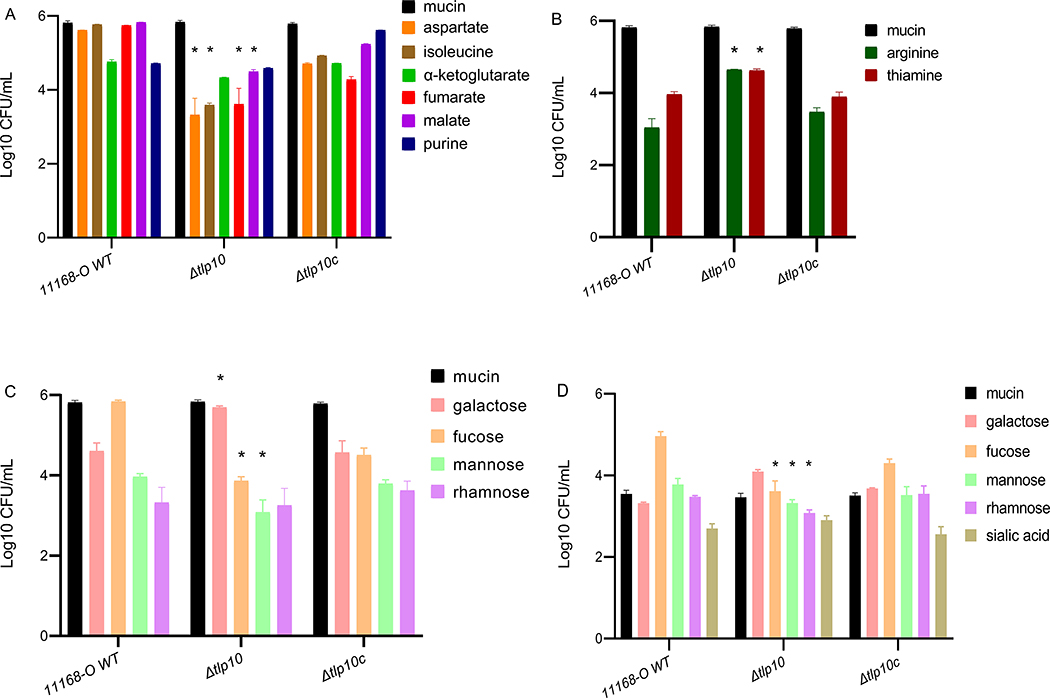
Fig. 2. Chemotaxis assays with wild-type and Tlp10 mutant C. jejuni.
(A and B) Wild-type C. jejuni strain 11168-O (11168-O WT), the isogenic Tlp10LBD mutant (Δtlp10), and the complemented mutant (Δtlp10c) were subjected to chemotaxis assays measuring the movement of starved cells towards test ligands considered attractants (A) and ligands considered repellents (B). (C) Chemotaxis to the monosaccharide ligands galactose, fucose, mannose, and rhamnose. The universal attractant mucin was used a positive control. The C. jejuni non-motile mutant (81116ΔflaA/flaB) and PBS were used as negative controls (Table S5). (D) μ-slide chemotaxis assays testing motility within a gradient of the test ligand were performed using galactose, fucose, mannose, rhamnose, and sialic acid as the test compounds. All data (Log 10 CFU/mL) represent three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate (n = 3). Asterisks indicate significant differences (P < 0.05; t-test).