Figure 4.
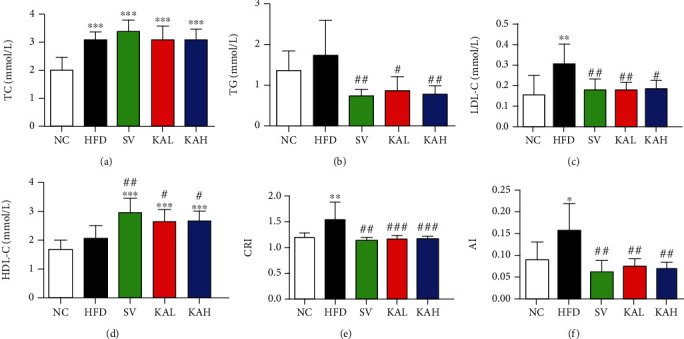
Effects of KA on HFD-caused the changes in blood lipid levels in mice: (a) total cholesterol (TC) in serum; (b) triglyceride (TG) in serum; (c) low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in serum; (d) high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) in serum; (e) coronary artery risk index (CRI); (f) atherosclerosis index (AI). In HFD mice, KAL and KAH significantly reduced serum TG level and significantly increased serum HDL-C, respectively. KAL and KAH significantly inhibited HFD-induced the increases of serum LDL-C, CRI, and AI levels, respectively. For HFD mice, these effects of KAL and KAH were similar to the effects of SV, respectively. Data were represented as mean ± S.D. (n = 5 for each group). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 vs. NC mice. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, and ###P < 0.001 vs. HFD mice.
