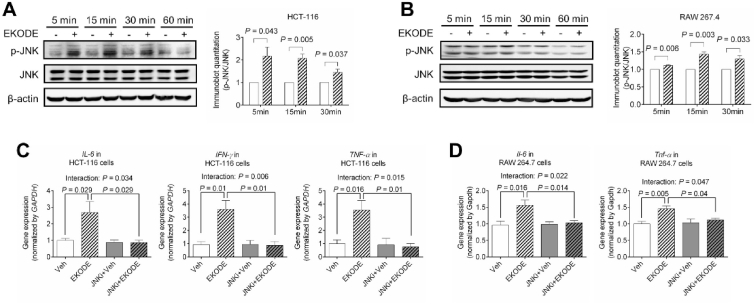
Fig. 8.
EKODE increases inflammation via JNK-dependent mechanisms in vitro. A-B, EKODE (concentration = 300 nM) increased JNK phosphorylation in HCT-116 and RAW 264.7 cells (n = 3 per group). C-D, Co-administration of a JNK inhibitor (SP600125, concentration = 100 nM) attenuated the pro-inflammatory effects of EKODE (300 nM) in HCT-116 and RAW 264.7 cells (n = 4–5 per group). The results are mean ± SEM. The statistical significance of two groups was determined using Student's t-test or Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test. Analysis of four groups was performed by two-way ANOVA. The cell culture experiments were performed with at least 3 independent repeats.