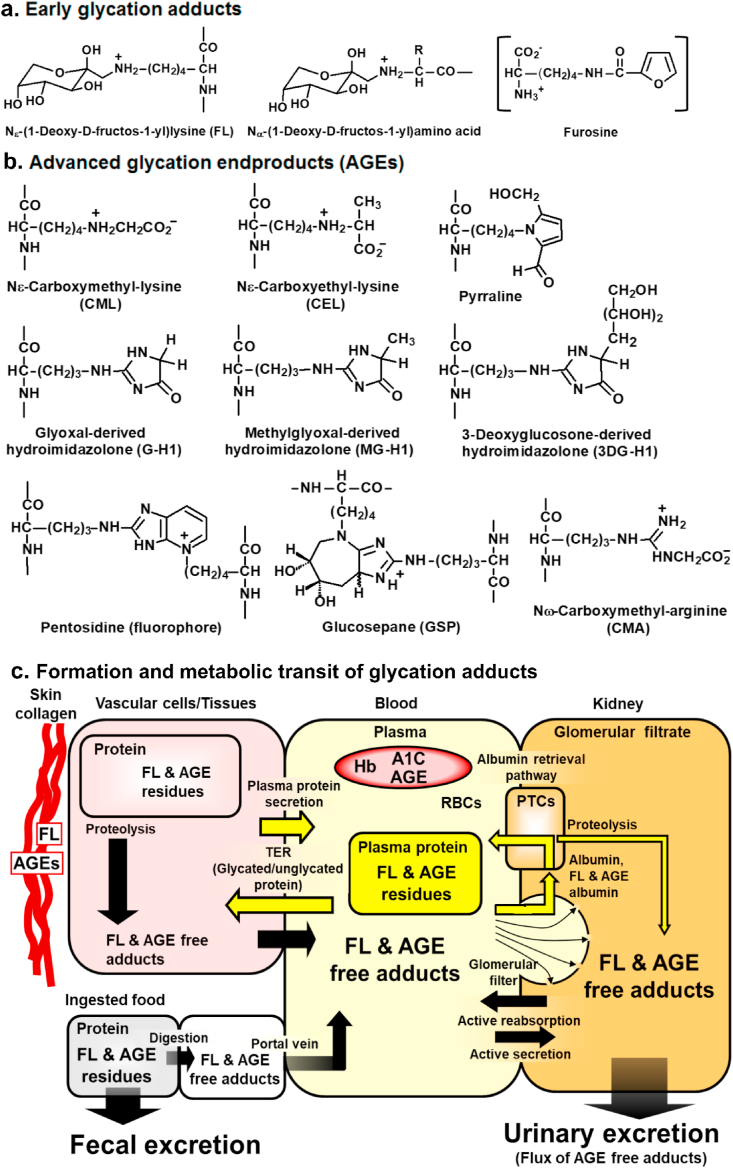
Fig. 1.
Protein glycation adducts (a. and b.)and formation, physiological processing and metabolic transit of glycated proteins(c.). Glycation adducts are shown as adduct residues with peptide bond linkage and ionization of glycation adducts at physiological pH, 7.4. For glycation free adducts, the peptide backbone N- and C-termini are –NH3+ and –CO2-, respectively. The square bracket round furosine indicates that it is an analytical surrogate (of FL), formed during acid hydrolysis in pre-analytic processing. Abbreviations: A1C, glycated hemoglobin HbA1c; PTC, proximal tubular epithelial cell; TER, transcapillary escape rate.