Figure 4.
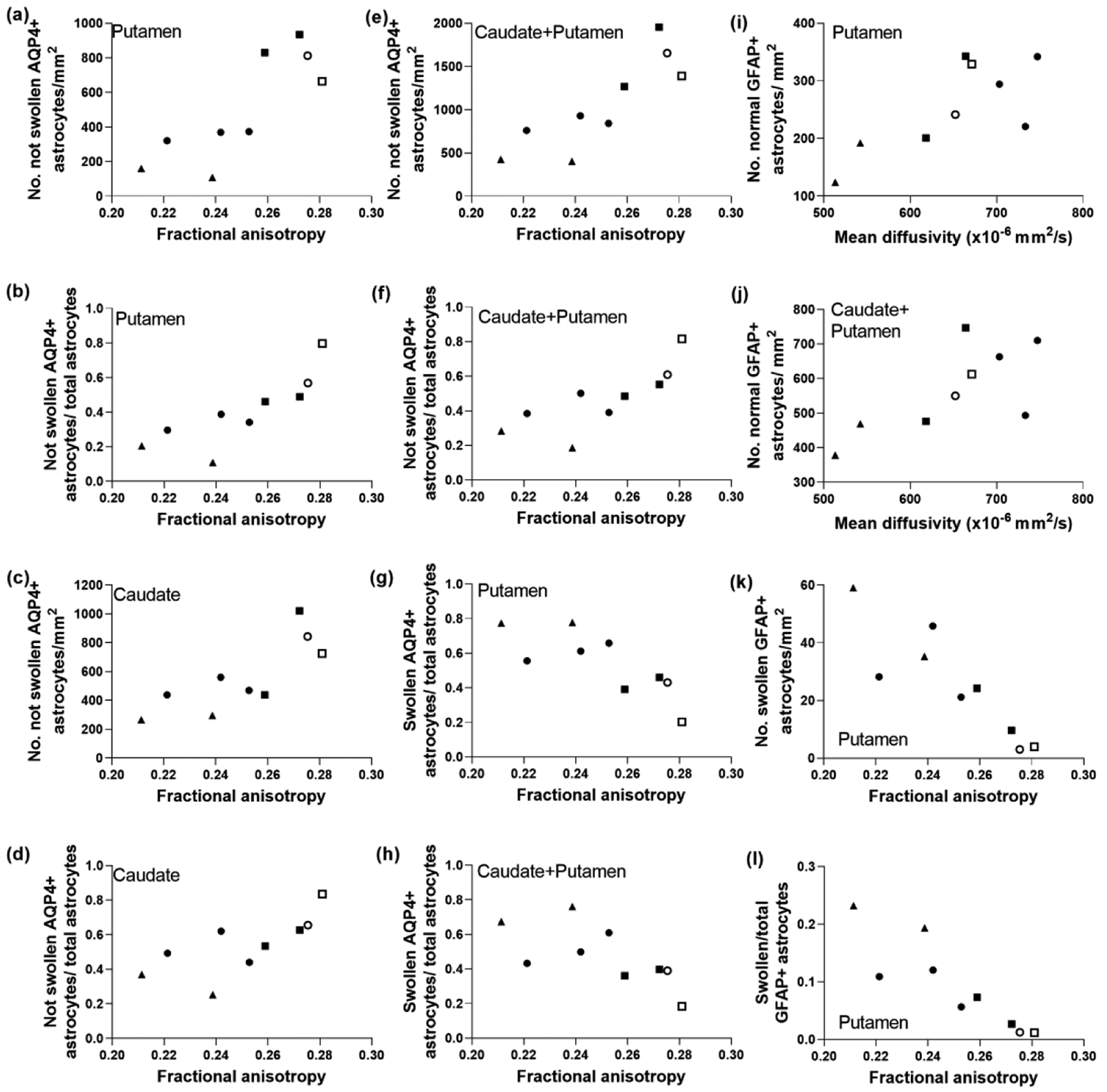
The morphology and number of aquaporin 4 (AQP4)- and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)-labeled astrocytes correlated with diffusion tensor imaging in piglets with striatal encephalopathy. Astrocytes were classified as being positive or negative for AQP4 and as being swollen or not swollen. (a, b) In putamen, the number of AQP4+ astrocytes without swelling (r=0.800; p=0.014) and the ratio to total astrocytes (r=0.933; p=0.001) positively correlated with fractional anisotropy (FA). (c, d) Similar relationships were observed in caudate, as FA correlated with the number of non-swollen AQP4+ astrocytes (r=0.820; p=0.010) and with the ratio of non-swollen AQP4+ astrocytes to total astrocytes (r=0.850; p=0.006). (e, f) FA correlated with the sum counts of AQP4+ astrocytes without swelling in putamen and caudate (r=0.867; p=0.005) and the ratio (r=0.900; p=0.002). (g) The number of swollen AQP4+ astrocytes in putamen inversely correlated with FA (r= −0.800; p=0.014). (h) The ratio of swollen AQP4+ astrocytes to total astrocytes in putamen and caudate also negatively correlated with FA (r= −0.800; p=0.014). The number of normal GFAP+ astrocytes in the putamen (i; r=0.700; p=0.043) and putamen and caudate (j; r=0.717; p=0.037) correlated with mean diffusivity. In putamen, the number of swollen GFAP astrocytes (k; r= −0.900; p=0.002) and the swollen-to-total GFAP+ astrocyte ratio (l; r= −0.933; p<0.001) correlated with FA. Symbols indicate piglets that received QA (open circle: 240 nmol, solid circle: 720 nmol, and solid triangle: 960 nmol), HI (solid squares), or sham procedure (open square).
