Figure 4. Dysfunction of TMEM106B impairs formation, transport, and function of lysosomes.
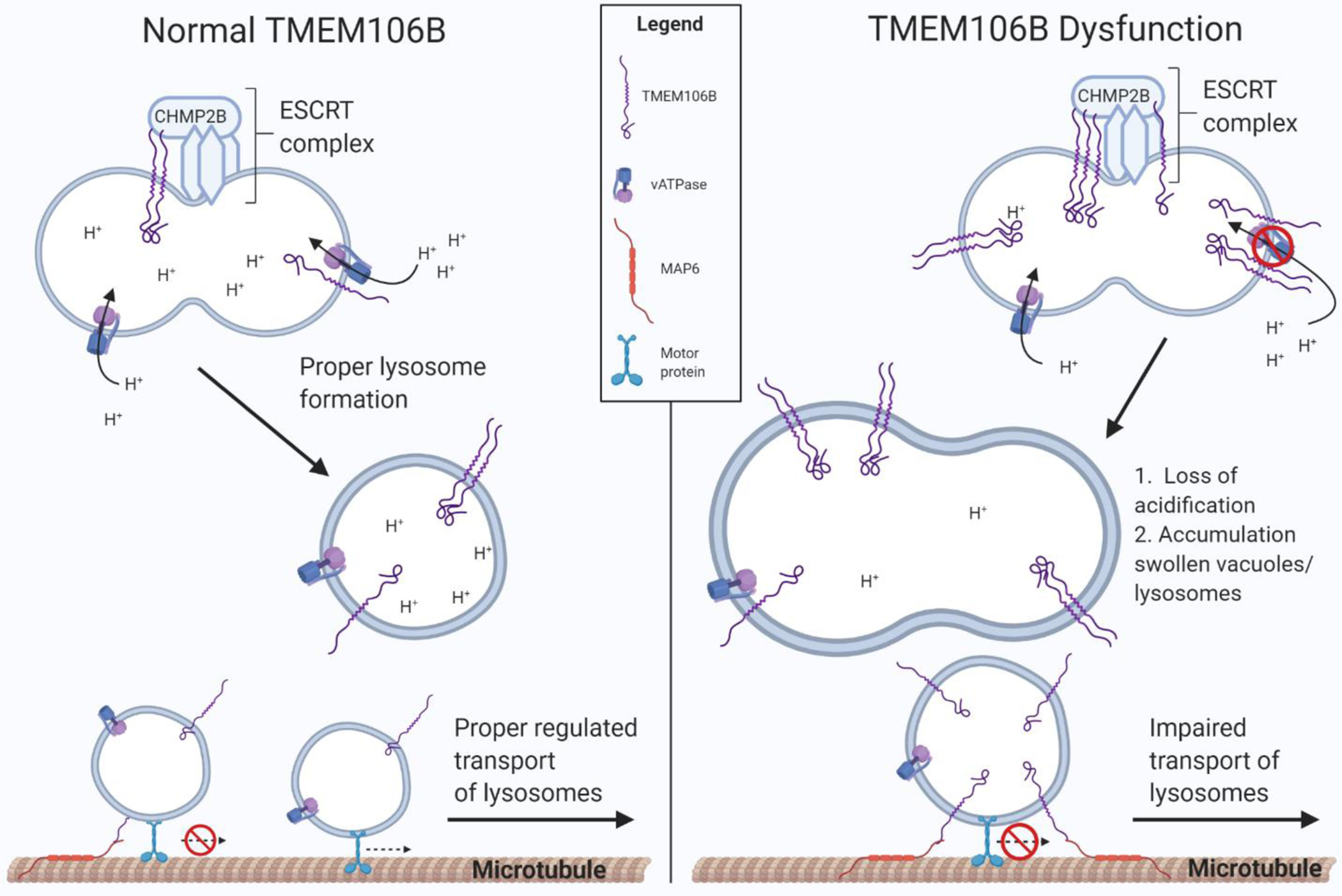
(Left panel) TMEM106B plays an important regulatory role in lysosome function, possibly through interaction with CHMP2B, a member of the ESCRT-III complex, and with V-ATPase, which is critical for proper lysosome formation. TMEM106B is also thought to bind microtubule-associated protein 6 (MAP6), a protein that stabilizes microtubules and regulates lysosome trafficking in neurons. (Right panel) Elevated TMEM106B levels, thought to be increased by the TMEM106B risk allele, or loss of TMEM106B function, causes impaired lysosome acidification and transport, leading to dysfunction and accumulation of swollen vacuoles and lysosomes.
