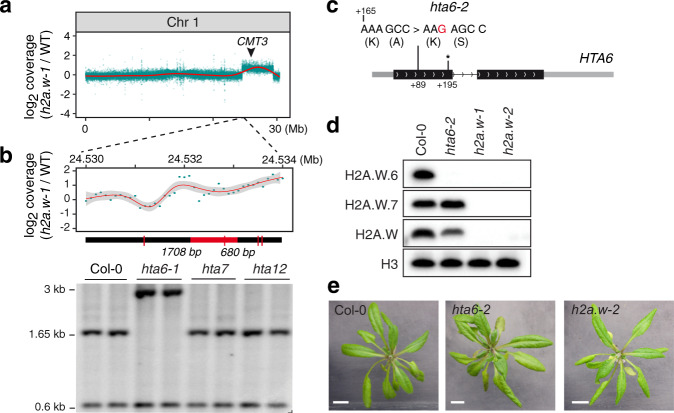
Fig. 1. H2A.W is not required for Arabidopsis development.
a Sequencing coverage of published h2a.w-1 BS-seq data22, averaged in 1 kb bins across chromosome 1. The red line shows the smoothed conditional mean (LOESS). The black arrowhead indicates the genomic location of CMT3. See also Supplementary Fig. 1a. b Zoomed-in view of plot in a across the left border of the chromosome 1 region showing increased coverage in h2a.w-1 (top panel). DNA gel blot analysis of the chromosome 1 region showing abnormal coverage in h2a.w-1 in the indicated T-DNA insertion mutants (lower panel). Genomic DNA of the indicated genotypes was digested with SspI (recognition sites indicated by red ticks on the thick black line) and hybridized with a fragment corresponding to the genomic region indicated in red under the plot. Two independent experiments were performed with identical results. c The hta6-2 CRISPR-Cas9 mutant allele. Diagram of the HTA6 gene showing the insertion of a G (in red) in hta6-2, which creates a frame shift 89 bp downstream from the translation initiation site and an early stop codon (asterisk) 195 bp downstream from the translation initiation site. d Western blot showing total loss of H2A.W in h2a.w-1 and h2a.w-2. Nuclear extracts of the indicated genotypes were analyzed using antibodies directed against H2A.W.6, H2A.W.7, total H2A.W, and H3. Two independent experiments were performed with similar results. e Representative images of wild-type, hta6-2, and h2a.w-2 plants (scale bar = 1 cm). Both hta6-2 and h2a.w-2 mutants develop like wild-type Col-0 plants. Source data underlying Fig. 1b, d are provided as a Source Data file.