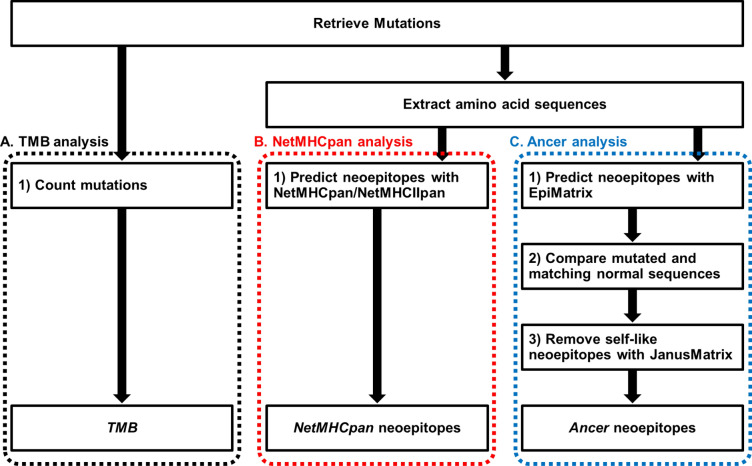
Figure 1.
BLCA mutanome analysis workflow. Mutations were retrieved for each patient sample and evaluated using three analysis workflows and then compared for overall survival and disease-free survival predictive accuracy. The three types of analyses were defined as follows: (A) “TMB analysis”: tumor mutational burden is evaluated from the count of mutations present in each tumor. (B) “NetMHCpan analysis”: mutation-bearing HLA class I and HLA class II ligands are identified with NetMHCpan 4.0 and NetMHCIIpan 3.1, respectively. This approach is similar to the one employed by the TCGA Research Network in their analysis of the BLCA cohort19. (C) “Ancer analysis”: mutation-bearing HLA class I and HLA class II ligands are identified with EpiMatrix, compared to matched normal sequences to identify Ancer-defined neoepitopes, and filtered with JanusMatrix to remove neoepitopes homologous to self.