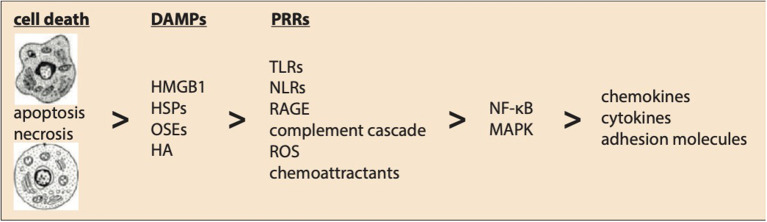
Figure 1.
Innate immunity following myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury. Ischemic-induced myocardial cell death activates innate immunity. Expression of endogenous ligands upon reperfusion are known as danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) including HMGB1, high-mobility group box-1; HSPs, heat shock proteins; OSEs, oxidation-specific epitopes; HA, hyaluronic acid. These DAMPs are recognized by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) like TLRs, NLRs, RAGE, complement cascade, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and chemoattractants. Finally, activation of the nuclear factor (NF)-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways induce the expression of pro-inflammatory chemokines, cytokines, and adhesion molecules regulating a complex post-ischemic inflammatory response.