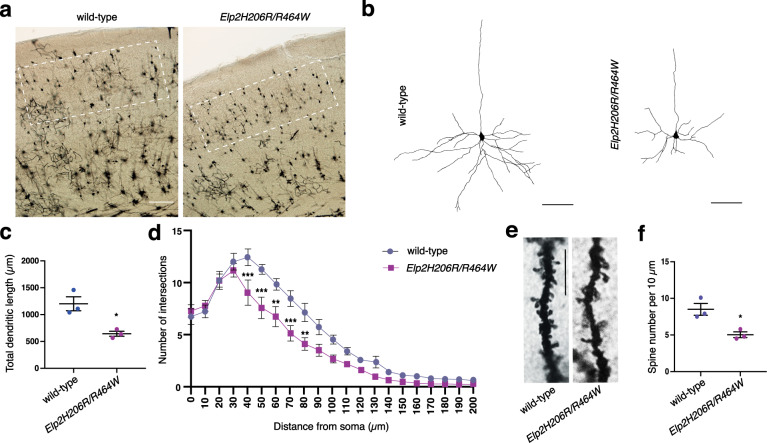
Fig. 6. Morphological abnormalities of cortical neurons in Elp2 mutant mice.
a Golgi-Cox-stained coronal sections in the area of the somatosensory cortex of adult (2-months-old) wild-type and Elp2H206R/R464W mice. White rectangles highlight pyramidal neurons from cortical layers II and III selected for neuron reconstruction and subsequent analyses. b Representative pyramidal neuron reconstructions are depicted (basal dendritic trees were reconstructed). c Quantification of total dendritic length from dendritic tree reconstructions shown in (b). n = 15, 5 neurons per animal and 3 animals per genotype. d Sholl analysis of the complexity of basal dendritic arbors. e Representative images of dendritic spines on basal dendrites of the cortical neurons shown in (a). f Spine density per 10 μm was measured on secondary dendrites. For (d) and (f) n = 30, 10 neurons per animal and 3 animals per genotype. Scale bars, 100 μm (a), 50 μm (b), and 10 μm (e). Statistical analysis: unpaired two-tailed t-test (α = 0.05) with Welch’s correction. Holm-Sidak correction was applied to adjust for multiple comparisons (d). Statistically significant differences are indicated (*p ≤ 0.05: for (c) p = 0.0379 and for (f) p = 0.0328; **p ≤ 0.01: for 60 μm p = 0.002599 and for 80 μm p = 0.003315; ***p ≤ 0.001: for 40 μm p = 0.000712, for 50 μm p = 0.000172 and for 70 μm p = 0.000930). Data represent mean ± SEM. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.