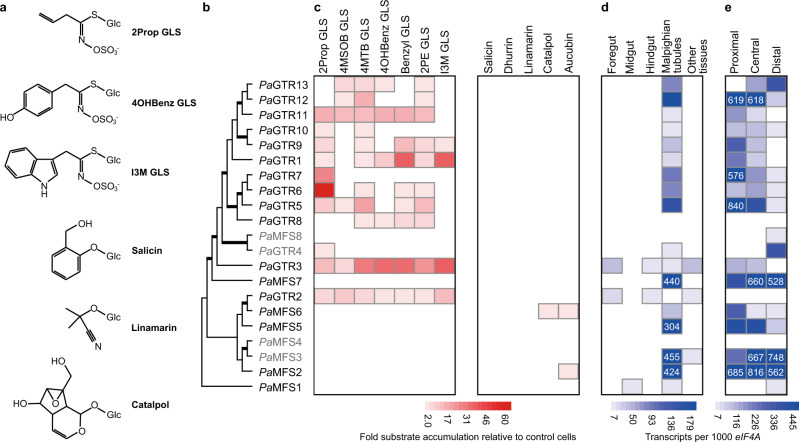
Fig. 1. Import activity and expression pattern of candidate MFS transporters.
a Chemical structures of selected glucosinolates (GLS) and nonhost glucosides used in transport activity assays. b Phylogenetic relationships of candidate transporters selected based on the diversification pattern of coleopteran MFS transporters shown in Supplementary Data 3. Branches shown in bold have a bootstrap support >95%. Recombinant proteins expressed in High Five insect cells were detected by Western blotting. For four candidates, we did not detect recombinant protein (Supplementary Fig. 1); the names of these candidates are written in gray. c Recombinant transporters were screened for glucoside uptake activity in assays using equimolar mixtures of glucosinolates or nonhost glucosides. Glucoside accumulation in transfected insect cells is expressed relative to that in mock-transfected insect cells used as background control. Values represent the mean of three assays. d Expression pattern of candidate MFS transporter genes in different tissues of P. armoraciae. e Expression pattern of candidate MFS transporter genes in different regions of the Malpighian tubule. Copy number estimates are given per 1000 copies of mRNA of the reference gene eIF4A. Low gene expression levels are visualized by limiting the scale to a value of 200 and 500 in (d) and (e), respectively. The exact values are provided for genes with higher expression levels. Each value represents the mean of four and three biological replicates in (d) and (e), respectively. 2Prop 2-propenyl, 4MSOB 4-methylsulfinylbutyl, 4MTB 4-methylthiobutyl, 4OHBenz 4-hydroxybenzyl, 2PE 2-phenylethyl, I3M indol-3-ylmethyl.