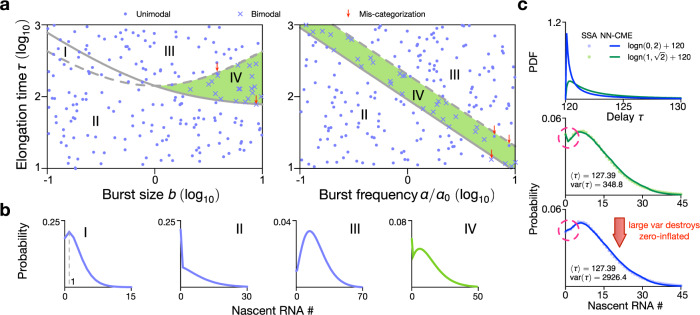
Fig. 5. Stochastic bifurcation diagram for Model III in the bursty regime (σoff ≫ σon) using the NN-CME and comparison with theory.
a From an analytical approximation of Model III in the bursty regime, the space is divided into four regions according to the type of distributions (shown in b): type I, a unimodal distribution with mode = 1; type II, a unimodal distribution with mode = 0; type III, a unimodal distribution with mode > 1; type IV, a bimodal distribution with two modes at zero and a non-zero value. Region IV is highlighted in green since it is a phase that does not exist in the bursty regime of the standard model of gene expression (Model III with delayed degradation replaced by first-order degradation)—this is hence delay-induced bimodality. The lines defining the division of space are: solid line is and the dashed line is , which respectively are the lower and upper bounds on τ given by Eq. (9). To check the accuracy of the ANN-aided model approximation for Model III, we used it to compute the NN-CME and then solved using FSP to obtain nascent number distributions for 200 points in parameter space. These are randomly sampled from the space {ρ = 2.11, σoff ∈ 2.11 × [10−1, 10], σon = 0.0282, τ ∈ [10, 103]} (left) and {ρ = 2.11, σoff = 0.609, σon = 0.0282 × [10−1, 10], τ ∈ [10, 103]} (right). Dots denote parameter sets for which the NN-CME distributions are unimodal and crosses show those for which the distributions are bimodal. The fact that the vast majority of crosses fall in region IV and the dots outside of it shows that the NN-CME agrees with the analytical approximation of Model III (parameter sets, which mismatch between the NN-CME and theory, are highlighted with red arrows and are very few in number). Note in the left figure of (a), the burst frequency is fixed to α = 0.0282 (left) while in the right figure, we use α0 = 0.0282 and the burst size is fixed to b = 3.46. c The NN-CME is learnt from stochastic simulations of the delay model of Model III with the added feature that the elongation time τ is a random variable sampled from two different lognormal distributions (see top figure). In the middle and bottom figures, we show that the delay-induced bimodality (phase IV) disappears as the variance on the elongation time τ increases at constant mean. The rate constants and other parameters related to the ANN’s training are specified in SI Table 1.