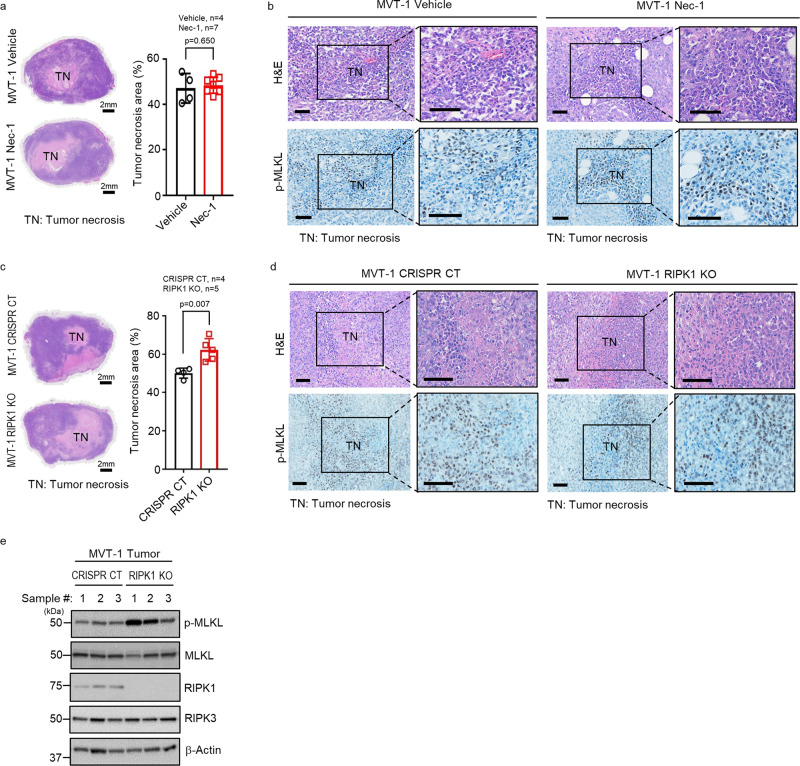
Fig. 1. RIPK1 is not required for MVT-1 mammary tumor necroptosis.
a FVB/NJ mice at three weeks post-implantation with MVT-1 cells were treated weekly with vehicle or Necrostatin-1 (Nec-1; i.v.) until week 5. Left panel shows the representative images of H&E stained 5-week tumors of vehicle or Nec-1 treated mice. Scale bar, 2 mm. Right panel shows the percentage of tumor necrosis area (TN) of the total tumor area from mice at 5-week. Data are presented as mean values ± SEM. b Representative H&E and immunohistological images of phospho-MLKL (p-MLKL) antibody staining of tumor sections from mice implanted and treated as in Fig. a. Scale bar, 50 µm. c MVT-1 CRISPR/Cas9 control (CRISPR CT) or MVT-1 RIPK1 knock out (RIPK1 KO) cells were generated by using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Left panel shows the representative H&E image of 4-week tumors from FVB/NJ mice implanted with the MVT-1 CRISPR CT or MVT-1 RIPK1 KO cells. Scale bar, 2 mm. Right panel shows the percentage of tumor necrosis area (TN) of the total tumor area after 4-weeks. Data are presented as mean values ± SEM. d Representative H&E and immunohistological images of p-MLKL antibody staining of 4-week tumor sections from mice implanted as in Fig. c. Scale bar, 50 µm. e Western blotting analysis of tumor lysates from mice implanted as in Fig. c using the indicated antibodies. Western blotting analysis representative of three independent experiments. Two-sided student’s t test was used to determine the statistical significance of differences between groups. Differences with P values < 0.05 were considered significant. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.