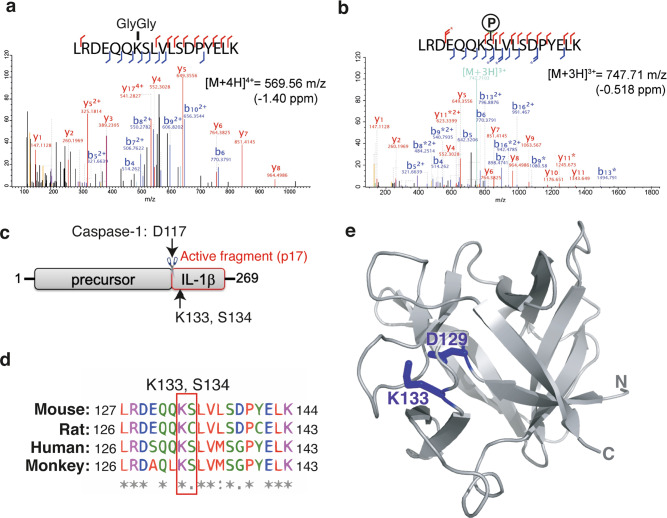
Fig. 4. IL-1β lysine 133 is ubiquitylated and forms an electrostatic interaction with aspartate 129.
a, b N-terminal FLAG tagged IL-1β was expressed in 293T cells and treated with MG132 (20 μM) for 6 h. FLAG-immunoprecipitated IL-1β was run on a SDS-PAGE gel and in-gel trypsin digestion performed on SYPRO Ruby stained protein bands corresponding to the molecular weight of precursor IL-1β and modified IL-1β. Samples were then analyzed by high-resolution mass spectrometry to identify IL-1β modification sites, particularly ubiquitylation sites (marked by a K-ε-GG linkage). MS/MS spectra indicate that IL-1β was ubiquitylated on K133 and phosphorylated on S134. Stars indicate neutral loss fragmentation ions, clearly demonstrating phosphate localization at serine 134. c Schematic of precursor IL-1β detailing the caspase-1 and -8 cleavage site (D117) and the location of K133 and S134 post-translational modifications within the C-terminal bioactive region. d Sequence alignment showing conservation of the region of IL-1β harboring K133 and S134 amongst mouse, rat, human and monkey species. e Structure of IL-1β (PDB: 2MIB) documenting the K133 and D129 electrostatic interaction.