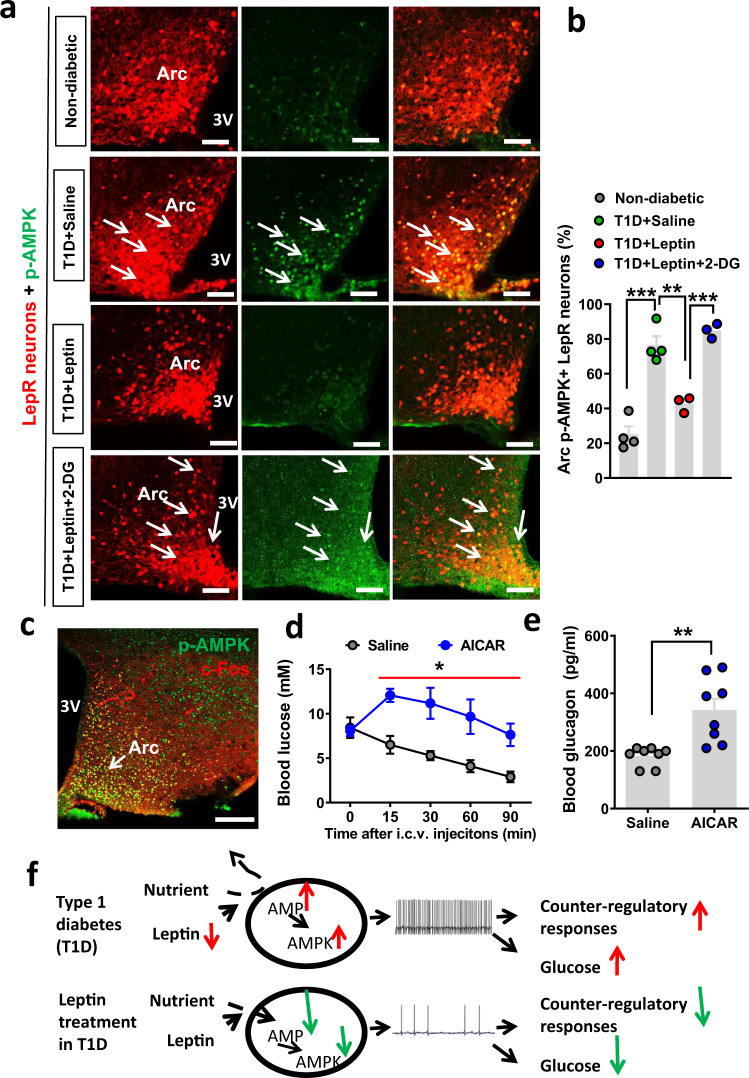
Fig. 7. T1D hyperglycemia and leptin action on reducing T1D hyperglycemia involve the AMPK pathway.
a Representative immunostaining images from n = 3–4 mice as shown in b for p-AMPK in hypothalamic sections were shown from control (a, Non-diabetic), T1D with saline treatment (a, T1D + saline), T1D with leptin treatment (a, T1D + leptin), and T1D with both leptin and 2-DG treatments (T1D + leptin+2-DG) at fed conditions. b Comparison in the percentage of LepRArc neurons with p-AMPK expression among the four groups (one-way ANOVA, n = 4 for nondiabetic controls and T1D-saline and n = 3 for T1D-leptin and T1D-leptin-2-DG, F(3, 10) = 42.27, ***P < 0.0001, nondiabetes vs T1D-saline; **P = 0.0051, T1D-saline vs T1D-leptin; ***P = 0.004, T1D-leptin vs T1D-leptin-2_DG). c Representative pictures from n = 1 mouse showing colocalization between p-AMPK (green) and c-Fos (red) in the Arc of T1D LepR-Cre mice. d, e Wild-type mice (8–9 weeks of age, males) were made T1D and then i.c.v. treated with leptin to restore euglycemia. These mice were then treated with i.c.v. injections of either saline or AICAR, an agonist of AMPK. Comparisons in blood glucose were shown following i.c.v. AICAR (d, two-way ANOVA, n = 3/each, F(1, 20) = 35.91, *P = 0.0374, saline vs AICAR at the 90-min time point) and in blood glucagon at 90 min after AICAR injection (e, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t tests, n = 8/each, t = 3.862, df = 14; n = 9/each, **P = 0.0017). f Diagram depicting hyperglycemia in T1D caused by heightened Arc GABAergic neuron activity due to energy deprivation and low leptin levels (top) and euglycemia restoration by leptin inhibition of neuron activity through reversing energy deprivation (bottom). 3: the third ventricle and Arc: arcuate nucleus. Data presented as mean ± SEM. 3V the third ventricle, Arc arcuate nucleus; Scale bar: 100 µM.