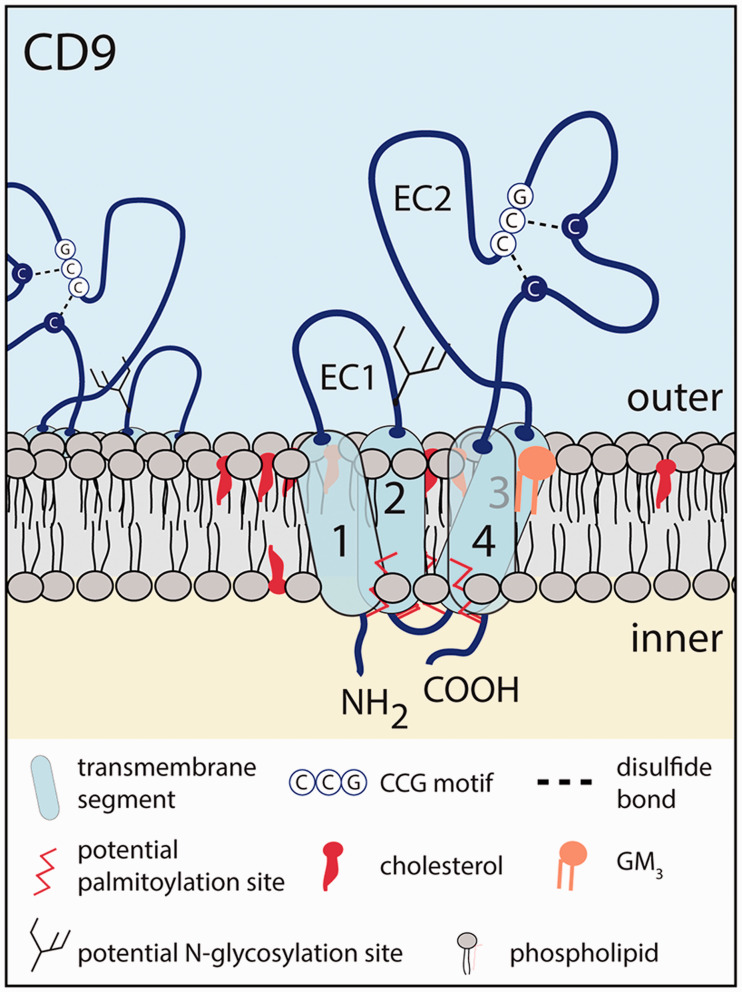
Figure 1.
Membrane topology of CD9. The human CD9 protein contains four transmembrane segments (1–4), short cytoplasmic N- and C-protein termini, and two extracellular (EC) domains forming a short and a larger loop. The CD9 EC2 domain is properly folded with two disulfide bridges in which two cysteine residues are found in a conserved CCG motif among all tetraspanins. A potential N-glycosylation site is located in the EC1 domain, close to the second transmembrane domain. Several cysteine residues at the transition of the cytoplasmic domains and transmembrane segments are subject to palmitoylation. The outer and inner leaflets of the plasma membrane are shown. Therein, membrane cholesterol and GM3 ganglioside could alter CD9 function. Note that the structure of CD9 is not represented with the appropriate scale.