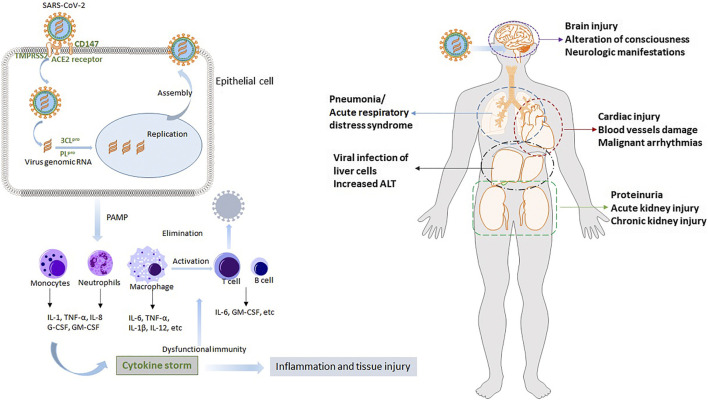
FIGURE 2.
The potential pathogenesis of COVID-19 and its pathophysiology. After SARS-CoV-2 infection, rapid innate immune response is activated. Then uncontrolled inflammatory responses cause cytokines storm, leading to acute lung injury such as severe respiratory failure. Other multiple organs, such as heart, liver and kidney, are also injured due to the virus and cytokines storm.