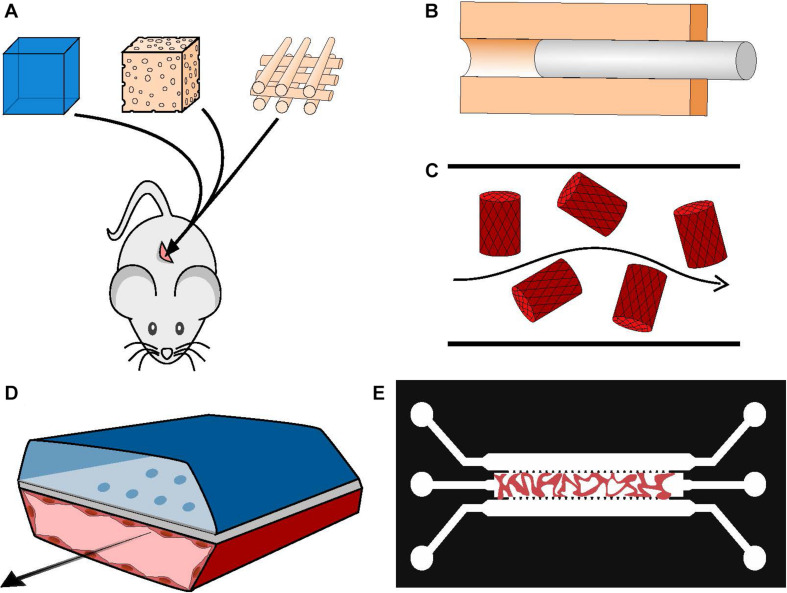
FIGURE 2.
Manufacturing vascularized BM systems. (A) Implantation of mesenchymal and endothelial cell-loaded hydrogels, sponges or printed scaffolds subcutaneously in immunodeficient mice. The resulting vasculature will be anastomosed to mouse host vasculature. (B) Generation of a hollow tube in a 3D matrix through the use of sacrificial material; the channel walls can be seeded with ECs afterward. (C) Cell-loaded hydrogel islets are seeded with a layer of ECs and placed in a microfluidic channel with a continuous flow, forming an inverted vascularized system (Khan et al., 2012). (D) Formation of organ-on-chip systems with two parallel hollow tubes separated by a porous membrane, one containing tissue specific cells and the other coated with ECs and perfused with medium to serve as a functional vascular system (Huh et al., 2013). (E) Generation of self-assembled and perfusable vascular network in a microfluidic chip (see dedicated Box 1).