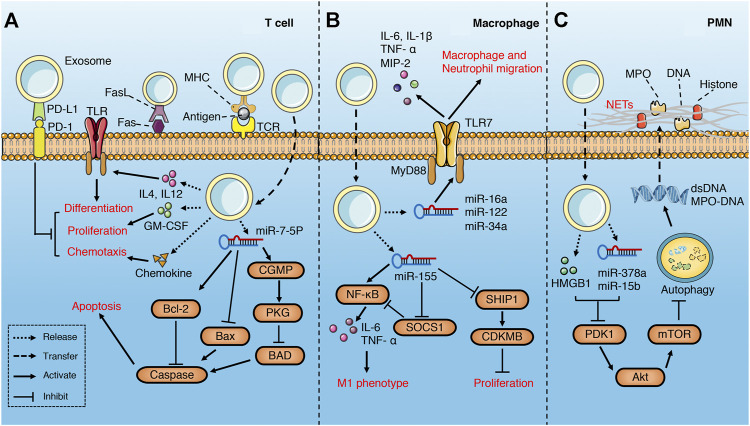
FIGURE 3.
Role of exosomes derived from serum in sepsis. (A) serum exosomes can promote differentiation, proliferation and chemotaxis of T cell via pro-inflammatory cytokines, GM-CSF and chemokines separately, while play the opposite role through PD1/PDL1 pathway. In addition, exosomes may attenuate T cell apoptosis through miR-7-5p-mediated inhibition of caspase. However, exosomes may also induce T cell apoptosis via FasL/Fas signaling pathway. (B) serum exosomes promote macrophage migration, proliferation and M1 polarization through multiple miRNAs-mediated signaling pathways. (C) Platelet exosomes induce excessive NETs formation through Akt/mTOR autophagy pathway.