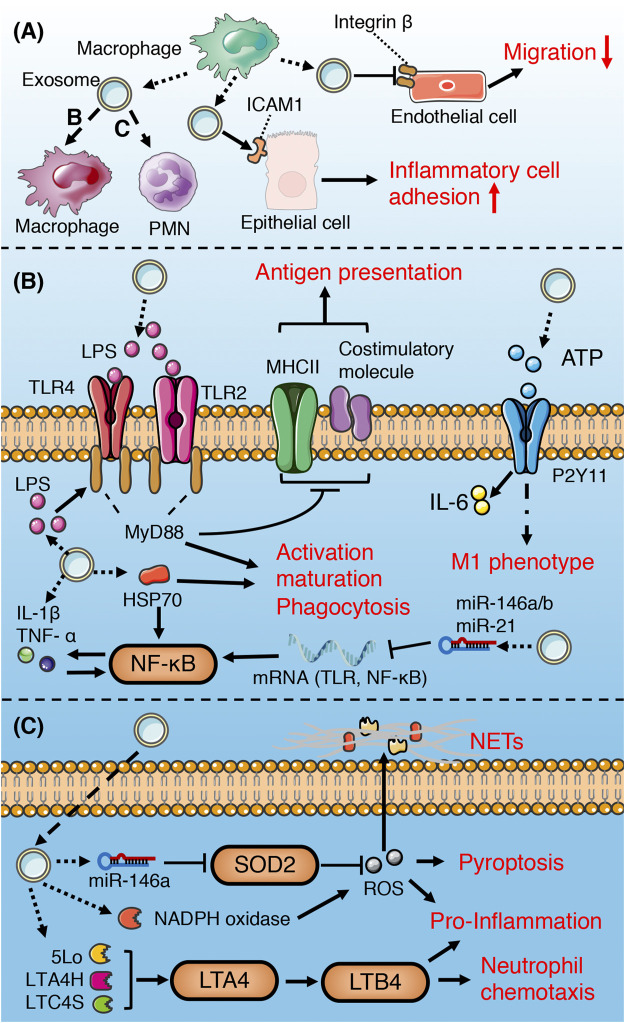
FIGURE 6.
Role of macrophage-derived exosomes in sepsis (A) macrophage-derived exosomes can induce pro-inflammatory response in recipient macrophage and PMN, promote inflammatory cell adhesion to endothelium, and suppress migration of epithelial cells (B) macrophage-derived exosomes containing DAMPs and PAMPs promote recipient macrophage activation, maturation, phagocytosis, and M1 polarization, while suppress the ability of antigen presentation. (C) Exosomal enzymes and miRNA increase NETs formation, chemotaxis, pro-inflammatory response, and pyroptosis of PMN.