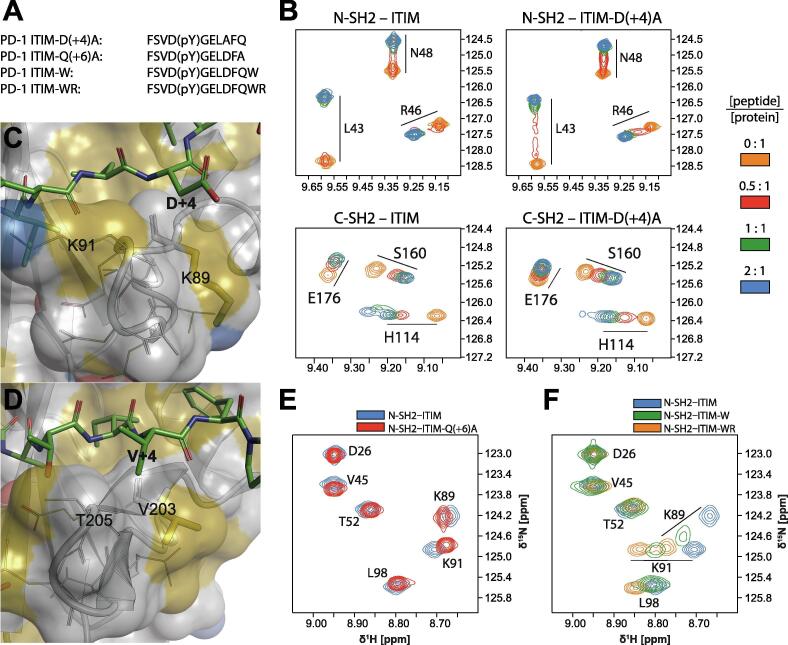
Fig. 3.
Influence of phosphopeptide side-chains at positions pY+4 and pY+6 on binding affinities. (A) Sequences of the ITIM mutants used to study the role of amino acids at position pY+4 and beyond pY+5. (B) 1H,15N-HSQC spectra of N-SH2 and C-SH2 in the presence of increasing concentrations of wild-type and D(+4)A ITIM. (C) Although not evident from the crystal structure, D(+4) may form transient electrostatic interactions with K89 and/or K91 of N-SH2; these interactions would not be possible with the D(+4)A mutation. (D) K89 and K91 in N-SH2 are replaced by V203 and T205 in C-SH2, which makes this area substantially more hydrophobic, in agreement with the high affinity of phosphopeptides possessing a hydrophobic residue at pY+4. (E) Overlay of 1H,15N-HSQC spectra of N-SH2 with a 2:1 peptide:protein molar ratio; the peptide is either wild-type ITIM or Q(+6)A ITIM. (F) Overlay of 1H,15N-HSQC spectra of N-SH2 with a 2:1 peptide:protein molar ratio; the peptide is either wild-type ITIM or mutant ITIM containing one (W) or two (WR) additional amino acids at the C-terminus. The protein concentration was 200 μM and all spectra were measured on a 600 MHz spectrometer at 298 K.