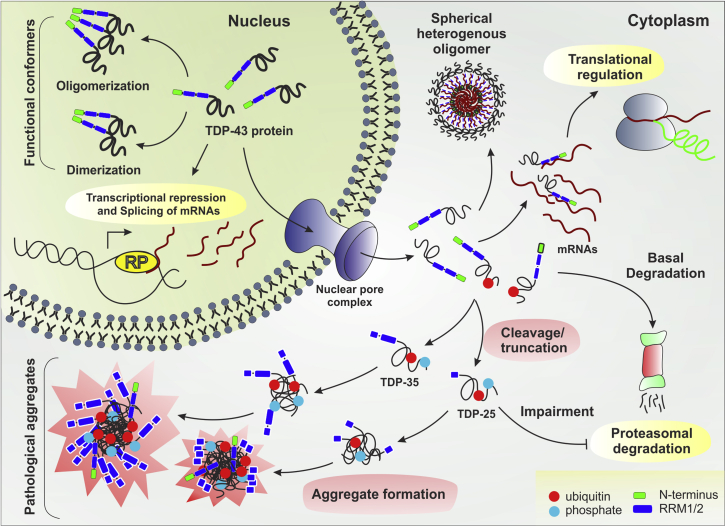
Figure 1.
Effects of TDP-43 truncation in disease pathogenesis
The scheme illustrates that TDP-43 functions normally as dimer or oligomer conformers in the nuclear compartment. However, upon translocation to the cytoplasm, truncation of TDP-43 promotes aggregation (gain-of-function). These aggregates hamper RNA stabilization in the cytoplasm leading to abnormal translational regulation, proteasomal degradation and sequestration/depletion of nuclear TDP-43 (loss-of-function). RP: RNA Polymerase complex.