Figure 5.
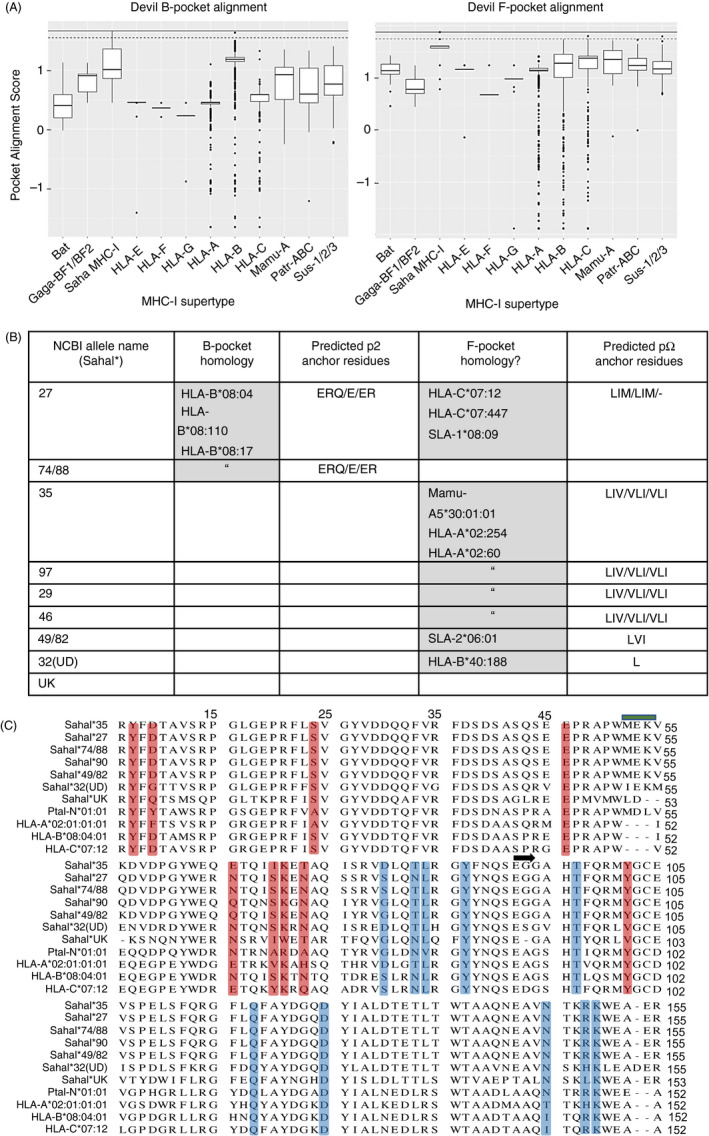
The F pocket of devil MHC‐I alleles is conserved with MHC‐I from eutherian mammals. (A) Binding pocket homology analysis of devil MHC‐I allele SahaI*27 against 16,748 MHC‐I sequences across 12 different MHC‐I supertypes from different species: Gaga = Gallus gallus, Mamu = Macaca mulatta, Patr = Pan troglodytes, Sus = Sus scrofa. Upper black line at the top of each box represents a perfect alignment score, data points above the tapered cut‐off line indicate sequence homology and were used to predict pocket motifs. (B) Table showing where homology was identified for B pocket and/or F pocket (grey boxes) for each devil MHC‐I allele; if predictions were possible, the respective motifs of the top 3 matches within that pocket have been included (p2/b pocket, pΩ/F pocket). The alleles with the highest homology to the devil are reported inside each grey box. (c) Multiple sequence alignment of α1‐α2 peptide binding groove region of devil MHC‐I alleles with selected human HLA alleles and the Ptal‐N*01:01 bat MHC‐I allele. HLA‐B*08 and HLA‐C*07 were included as they had the highest alignment scores to SahaI*27 with the B and F pocket, respectively. B pocket residues are highlighted in red, and F pocket residues are highlighted in blue. The blue bar denotes the 3aa insertion common to Ptal and devil MHC‐I sequences. A black arrow marks the beginning of the α2 domain
