Figure 7.
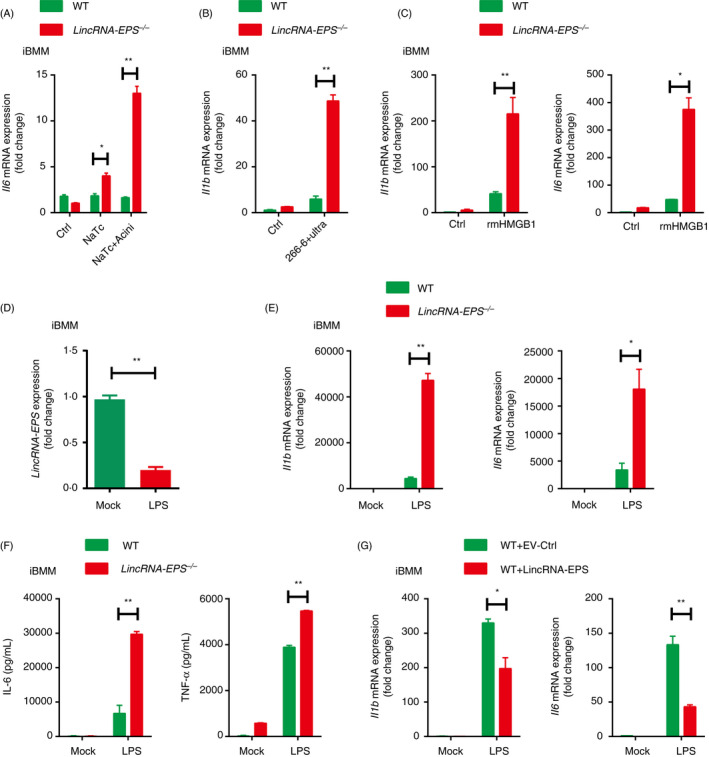
LincRNA‐EPS inhibits inflammatory cytokine production in response to HMGB1 and LPS stimulation in macrophages. (A) RT‐qPCR analysis of Il6 mRNA expression in the WT or lincRNA‐EPS‐/‐ iBMMs stimulated with 200 µM NaTc, or stimulated with the injured mouse acinar cells for 6 hr. The acinar cells were freshly isolated and pretreated with 200 µM NaTc for 2 hr. (B) RT‐qPCR analysis of Il1b mRNA expression in the WT or lincRNA‐EPS‐/‐ iBMMs cocultured with the ultrasonic damaged 266‐6 cells for 6 hr. (C) RT‐qPCR analysis of Il1b and Il6 expression in the WT or lincRNA‐EPS‐/‐ iBMMs stimulated with rmHMGB1 (500 ng/ml) for 6 hr. (D) RT‐qPCR analysis of lincRNA‐EPS transcripts in the WT or lincRNA‐EPS‐/‐ iBMMs stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 6 hr. (E) RT‐qPCR analysis of Il1b and Il6 mRNA expression in the WT or lincRNA‐EPS‐/‐ iBMMs stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 6 hr. (F) ELISA measurement of IL‐6 and TNF‐α in the supernatant of WT or lincRNA‐EPS‐/‐ iBMMs stimulated with LPS(100 ng/ml) for 24 hr. (G) RT‐qPCR analysis of Il1b and Il6 mRNA expression in the empty vector control (EV‐Ctrl) or lincRNA‐EPS rescued lincRNA‐EPS‐/‐ iBMMs stimulated with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 6 hr. Data are shown as mean ± SEM from at least three independent experiments. *P < 0·05 and **P < 0·01 by unpaired Student's t‐test.
