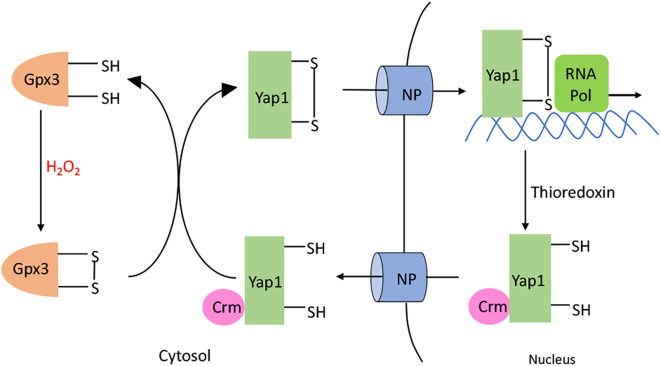
Figure 8.
Yap1p activation. H2O2 oxidizes the C36 residue of glutathione peroxidase (Gpx3). The resulting sulfenate interacts with C598 in the C-terminal domain of Yap1p to form a intermolecular disulfide bond. Subsequent thiol-disulfide exchange reactions produce C303-C598 and C310-C629 disulfide bonds in Yap1p. Yap1p accumulates in the nucleus, leading to the activation of the Yap1p regulated genes. When H2O2 diminishes, Yap1p is reduced by the thioredoxin system; this change makes its nuclear export signal accessible to Crm, causing Yap1p to be transported back out of the nucleus.