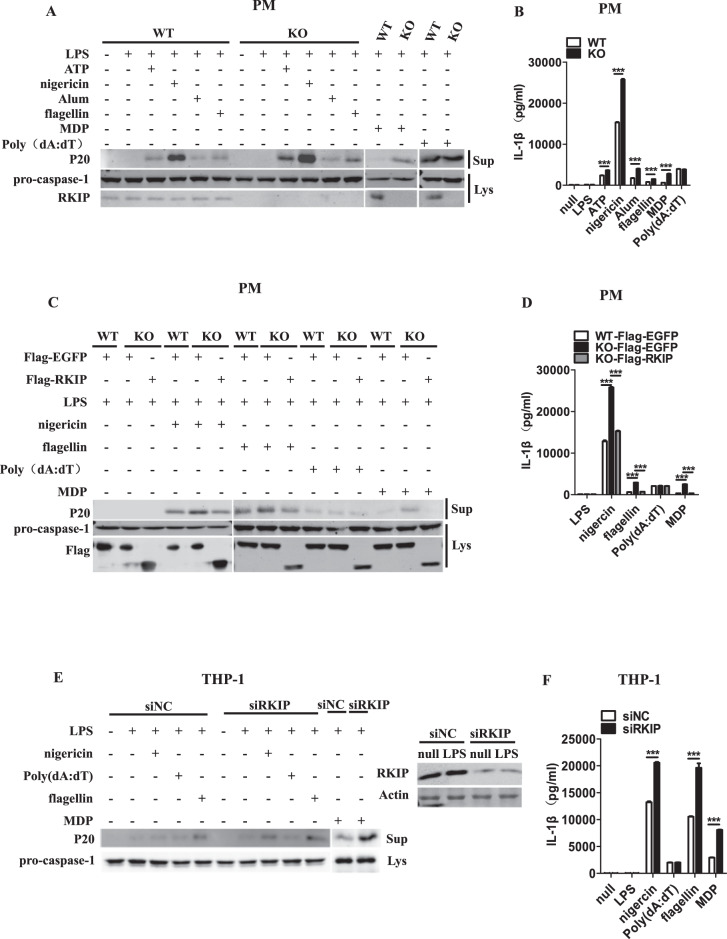
Fig. 1.
RKIP inhibits the activation of the NLRP3, NLRC4 and NLRP1 inflammasomes but not the AIM2 inflammasome. a, b A total of 1 × 106 wild-type (WT) or Rkip-knockout (KO) peritoneal macrophages (PMs) were primed with LPS (1 µg/ml) for 4 h and then treated with ATP (5 mM), nigericin (Ni) (20 µM), Alum (300 µg/ml), flagellin (1 µg/ml), poly(dA:dT) (5 µg/ml), and MDP (500 µg/ml) for the indicated times. Immunoblotting analysis of the supernatants (Sup) and cell extracts (Lys) (a) and ELISAs of the supernatants (Sup) were performed to assess IL-1β release (b). c, d WT or Rkip-KO PMs (1 × 106) were transfected with Flag-EGFP or Flag-RKIP. Forty-eight hours later, the transfectants were primed with LPS (1 µg/ml) and then treated with nigericin (Ni) (20 µM), flagellin (1 µg/ml), poly(dA:dT) (5 µg/ml) and MDP (500 µg/ml) for the indicated times. Immunoblotting analysis of the supernatants (Sup) and cell extracts (Lys) (c) and ELISAs of the supernatants (Sup) were performed to assess IL-1β release (d). e, f THP-1 cells (1 × 106) were differentiated with 100 nM PMA overnight in 12-well plates, transfected with a specific siRNA for RKIP, primed with LPS (1 µg/ml) and treated with nigericin (Ni) (20 µM), poly(dA:dT) (5 µg/ml), flagellin (1 µg/ml) and MDP (500 µg/ml) for the indicated times. Immunoblotting analysis of the supernatants (Sup) and cell extracts (Lys) (e) and ELISAs of the supernatants (Sup) were performed to assess IL-1β release (f). Data are the mean ± SEM (b, d, and f) and representative of three independent experiments. Student’s t test was used for statistical calculation. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001