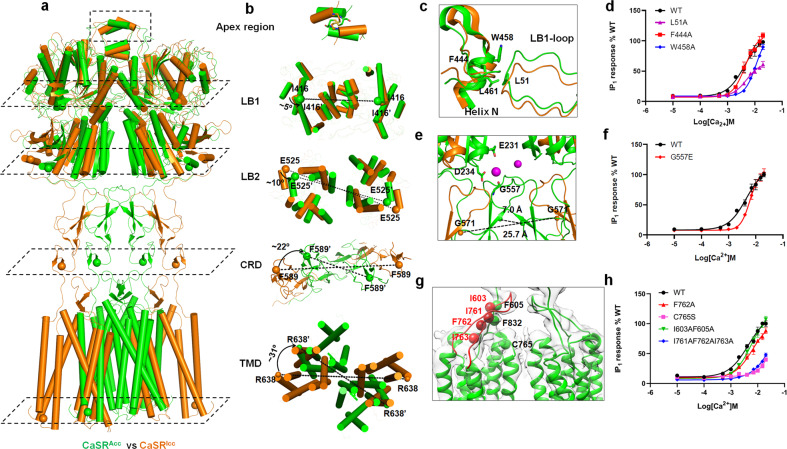
Fig. 4. Conformational changes of CaSR upon Ca2+ binding.
a Structural comparison of CaSR dimers in inactive (orange) and active (green) states. The dimeric CaSR structures are viewed in slices parallel to the membrane plane. b Gradual increase in the rotational angles of different subdomains down to the TMD along the symmetric axis of the inactive (orange) and active (green) CaSR dimers. The rotational angles of each subdomain are indicated. c Conformational changes of the interface between the LB1 loop and helix N. In Ca2+/L-Trp-bound active CaSR, the LB1 loop (green) reaches across the dimerization interface between two LB1 regions to contact helix N in the adjacent subunit, leading to domain rotation along the dimer axis. The LB1 loop and helix N in inactive CaSR are shown in orange. d Mutations of residues in hydrophobic sites in the LB1 loop (L51A) and helix N (F444A, W458A) reduced receptor activation by Ca2+. The IP1 accumulation data represent the means ± SD of three independent experiments. e Ca2+ ions were coordinated by D234, E231 in the LB2 region of one subunit, and G557 in the CRD of the other subunit, increasing the proximity of G557 residues of the two subunits in the active CaSR compared with that in the inactive CaSR. f The G557E mutation decreased the Ca2+-induced receptor response. The IP1 accumulation data represent the means ± SD of three independent experiments. g Structure model and cryo-EM map showing interactions between ECL2 of the TMD and the CRD. Critical residues at the CRD–TMD interface are shown as spheres at their Cα positions (I761, F762, I763, I603, and F605), indicating hydrophobic interactions between ECL2 and the linker region connecting the CRD and TMD. h Site mutations disrupting hydrophobic interactions between ECL2 and the CRD–TMD linker decreased the sensitivity of CaSR to Ca2+, as shown by Ca2+-stimulated IP1 accumulation assay. Data represent the means ± SD of three independent experiments.