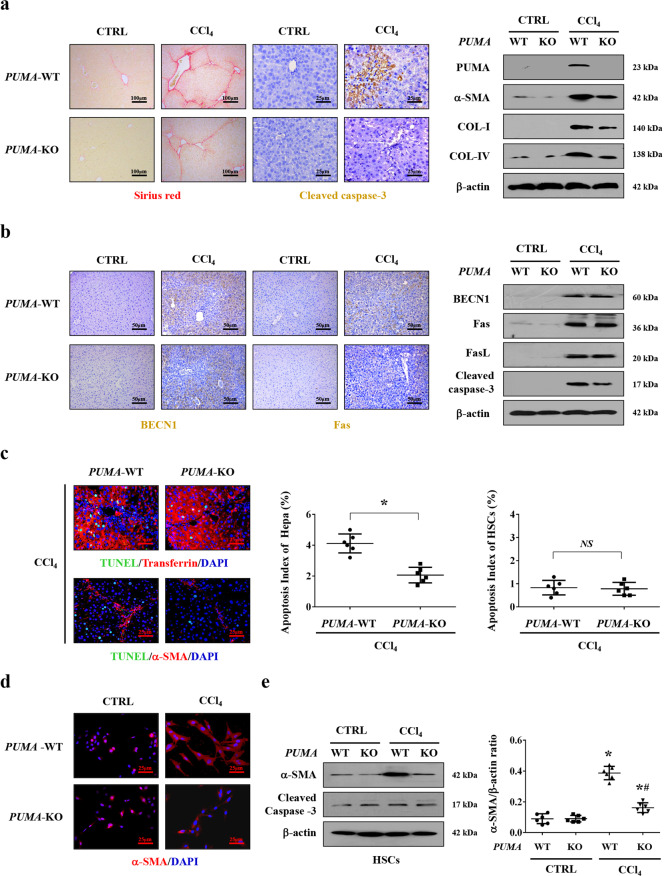
Fig. 4. Targeted deletion of PUMA ameliorated hepatocytes apoptosis and liver fibrosis.
a Sirius red staining (red) and cleaved caspase-3 staining (brown) presented that targeted deletion of PUMA ameliorated hepatic apoptosis and collagen deposition. Western blotting presented that targeted deletion of PUMA ameliorated the levels of collagen-IV (COL-IV), collagen-I (COL-I), and α-SMA in CCl4-treated mice (n = 6 per group). b Immunohistochemistry staining and western blotting revealed that PUMA deficiency did not affect the status of Fas and BECN1 in CCl4-treated mice. c Double immunofluorescence staining (transferrin (red) and TUNEL (green), α-SMA (red) and TUNEL (green)) and the analysis of the apoptotic index of hepatocytes or HSCs indicated that targeted deletion of PUMA mainly ameliorated hepatocytes apoptosis during liver fibrosis, n = 6 per group. Nuclei (blue) were counterstained with DAPI. *P < 0.05. NS, no significance. d α-SMA (red) staining in the primary HSCs dissociated from the indicated PUMA-WT and PUMA-KO mice was represented, nuclei (blue) were counterstained with DAPI. e The indicated proteins from primary HSCs analyzed by western blotting. The ratio of densitometry units of the normalized α-SMA/β-actin was also determined, n = 6 per group, values are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 versus primary HSCs from CTRL mice, #P < 0.05 versus primary HSCs from CCl4-treated PUMA-WT mice.