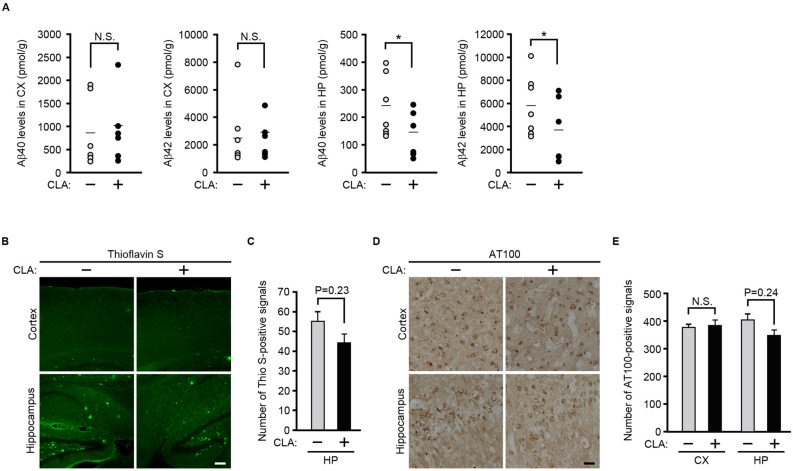
Figure 2.
The c-9, t-11-CLA diet reduces Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels in the hippocampus of AD model mice. (A) Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels were measured with ELISA using lysates of the cortex and hippocampus of c-9, t-11-CLA diet-fed AD model mice (CLA +) and control diet-fed AD model mice (CLA −). Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels in the hippocampus of c-9, t-11-CLA diet-fed mice were significantly decreased (right graphs) compared with controls, but were not significantly changed in the cortex (left graphs). Bars show the average value (n = 6 mice for each group). *P < 0.05 (Aβ40, P = 0.032; Aβ42, P = 0.031). (B) Thioflavin-S staining of brain sections of c-9, t-11-CLA diet-fed and control diet-fed AD model mice. The number of thioflavin-S-positive signals (green) tended to decrease in the hippocampus, but the positive signals were rarely detected in the cortex. (C) The histograms show the number of thioflavin-S-positive signals in the hippocampus. (n = 6 mice for each group; five different fields per mouse were used for counting of the positive signals). (D) Immunostaining of the brain sections of c-9, t-11-CLA diet-fed and control diet-fed AD model mice with AT100 antibody. The number of AT100-positive signals in the hippocampus of c-9, t-11-CLA diet-fed mice tended to decrease but no difference was seen in the cortex. (E) The histograms show the number of AT100-positive signals (n = 6 mice for each group; eight fields per mouse were counted). CX: cortex, HP: hippocampus. Bar, 50 µm. CLA + : c-9, t-11-CLA diet-fed AD model mice. CLA − : control diet-fed AD model mice.