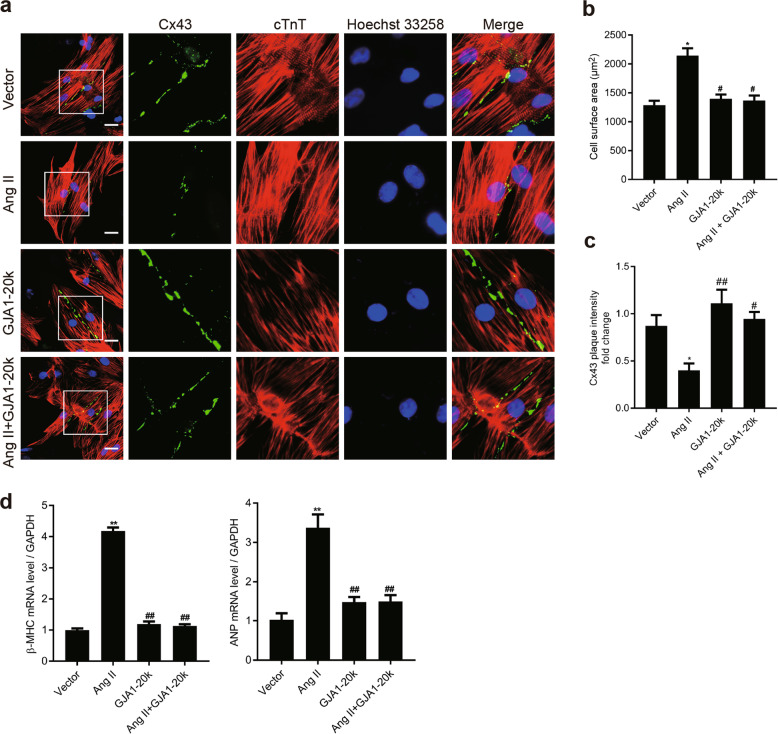
Fig. 5.
GJA1-20k attenuates angiotensin II (Ang II)-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy (CH) by promoting gap junction formation in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes (NRCMs). NRCMs were transfected with an empty control vector or a construct carrying GJA1-20k cDNA for 24 h and then treated with vehicle (DMSO) or Ang II (1 μM) for 48 h. a Immunofluorescence detection of Cx43 gap junctions (green); cTnT staining (red) was performed to identify cardiomyocytes (Bar = 20 μm). Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33258 (blue). b Quantification of the cell surface area (μm2) of 50 NRCMs in each group is shown. n = 3. *P < 0.05 vs. vector. #P < 0.05 vs. Ang II. c Quantification of Cx43 fluorescence intensity at cell–cell borders. *P < 0.05 vs. vector. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. Ang II. n = 3. d The β-myosin heavy chain (β-MHC) and atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) mRNA levels were measured by RT-qPCR. **P < 0.01 vs. vector. ##P < 0.01 vs. Ang II. n = 3. Data are presented as the means ± SEM.