Table 2.
Standard TTE images for the assessment of AS.
| View (modality) | Measurement | Explanatory notes | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parasternal long axis (PLAX); 2D | LV dimensions Calculate indexed LV mass using linear method | Visual assessment of wall motion Calcification of aortic valve (see ‘Calcification and aetiology of AS’ section) Indexed LV mass is a prognostic marker in AS (see ‘Additional prognostic markers’ section) | 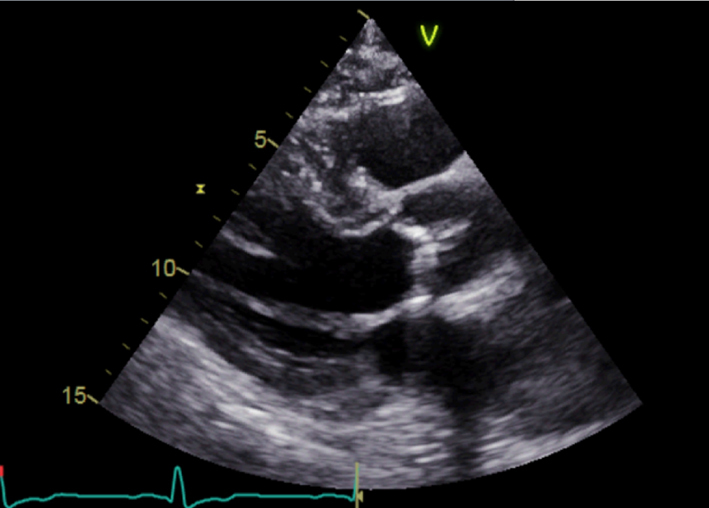 |
| Parasternal long axis; zoom 2D | Assess calcification and mobility of cusps Advanced AS unlikely without significant cusp calcification or restriction Assess for central vs eccentric closure line suggesting BAV (‘Anatomy’ section) | 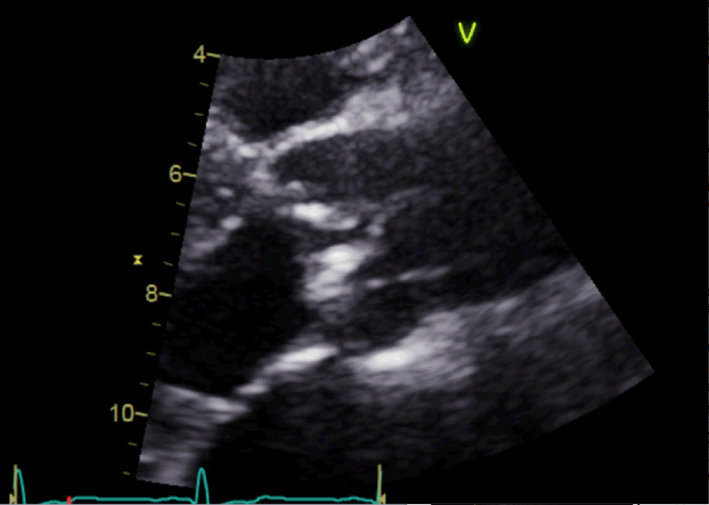 |
|
| Parasternal long axis; zoom 2D with colour Doppler | Assess for turbulence and presence of aortic regurgitation | 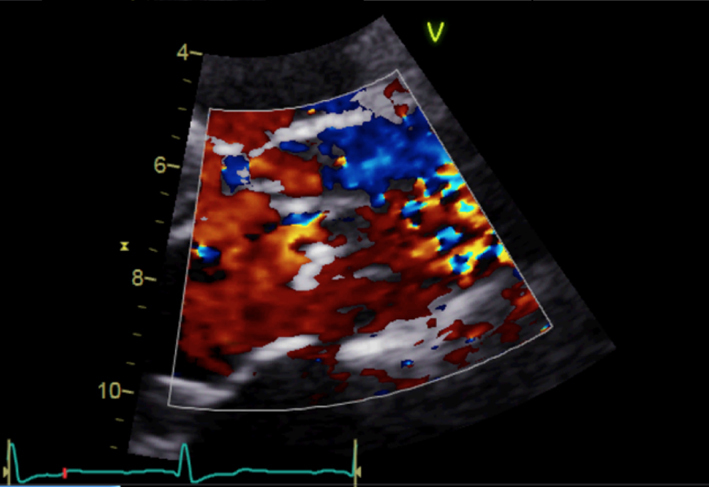 |
|
| Parasternal long axis; zoom 2D | LVOT dimension for assessment of AVA and stroke volume | Obtained at level of cusp insertion Inner-edge to inner-edge in mid-systole when LVOT is at a maximum Measurement parallel to aortic valve See ‘Essential parameters in the echocardiographic assessment of AS severity’ section | 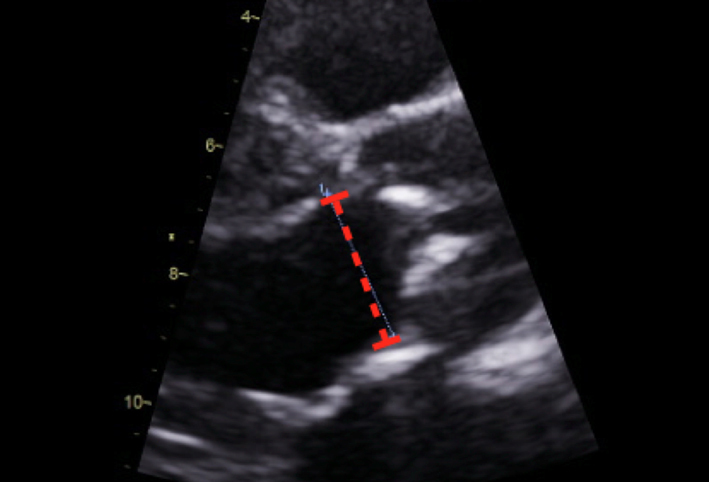 |
| Parasternal long axis; zoom 2D | Measurement of the aorta including the sino-tubular junction | Inner-edge to inner-edge method in end-diastole May be used in the assessment of the energy loss index (ELI; see ‘Additional parameters in the assessment of aortic valve stenosis’ section) | 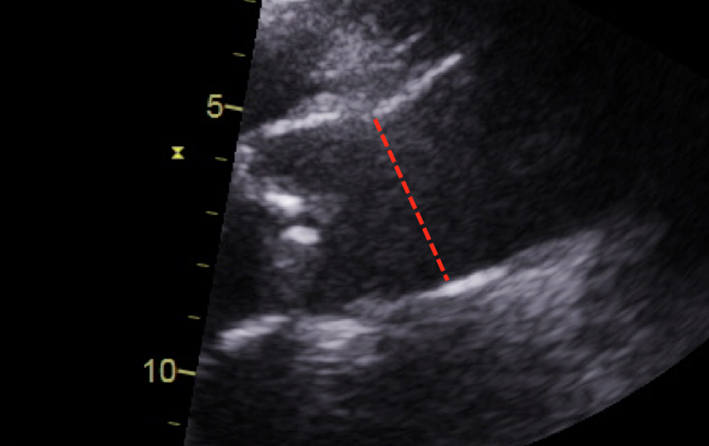 |
| Parasternal short axis (PSAX); 2D | Overview Visual appearance of aortic valve – cusp calcification and mobility | 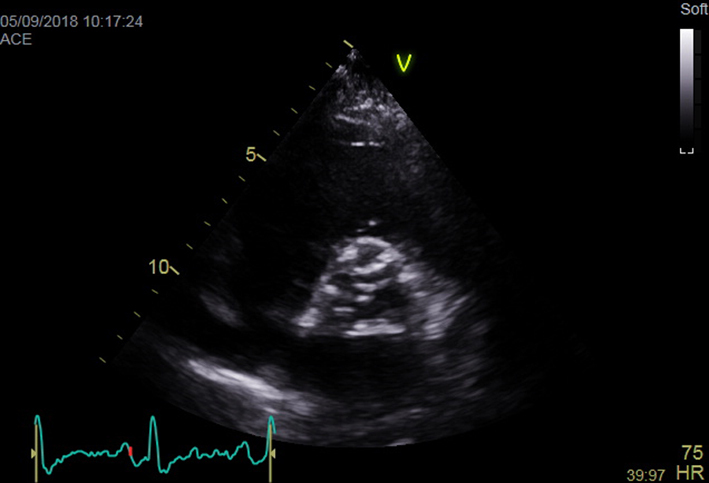 |
|
| Parasternal short axis; zoom 2D (+ colour Doppler) | Morphology of valve Visual appearance of calcification and mobility of cusps Colour Doppler to assess for presence and origin of AR | 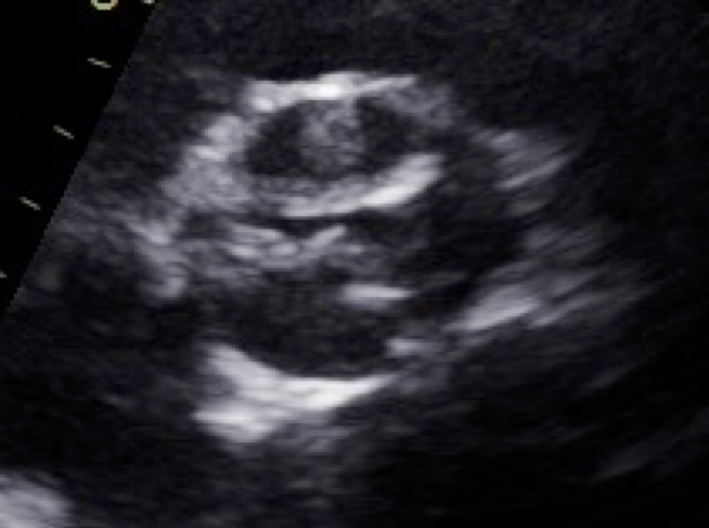 |
|
| Apical 4-chamber view; 2D imaging optimized for LV assessment | LV volumes and LVEF using quantitative methodology Consider GLS | LVEF is a prognostic marker in AS (see ‘Additional prognostic markers’ section) GLS is a potential marker of prognosis in AS (see ‘Additional prognostic markers’ section) | 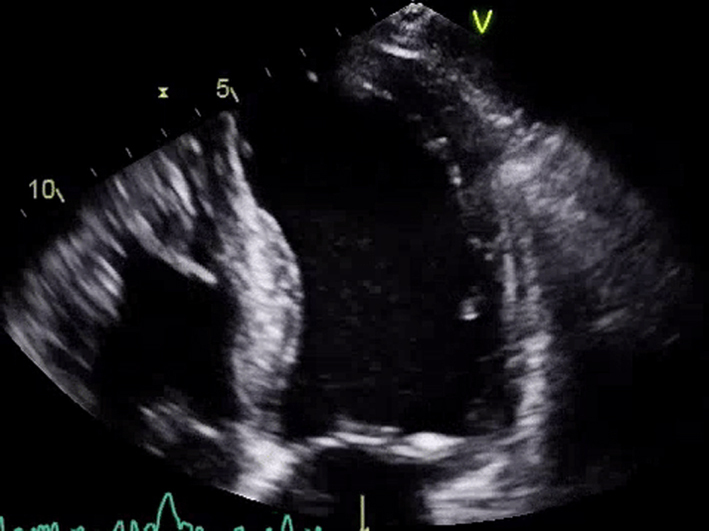 |
| Apical 5-chamber view; 2D imaging (+ colour Doppler) | Overview Visual appearance of aortic valve – cusp calcification and mobility Colour Doppler assessment for AR | 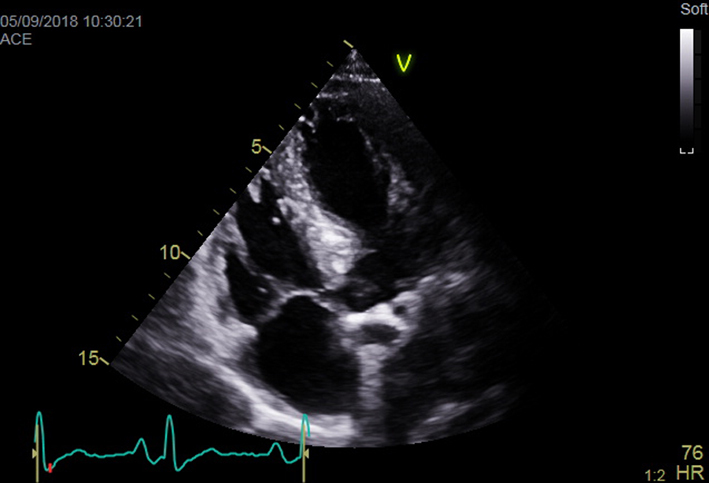 |
|
| Apical 5-chamber view; 2D imaging zoom | CW Doppler tracings for AV Vmax and mean AVG | Sweep speed 50–100 mm/s Trace around dense aspect of Doppler curve Average of three tracings in sinus rhythm (SR) See ‘Essential parameters in the echocardiographic assessment of AS severity’ section for optimization and troubleshooting | 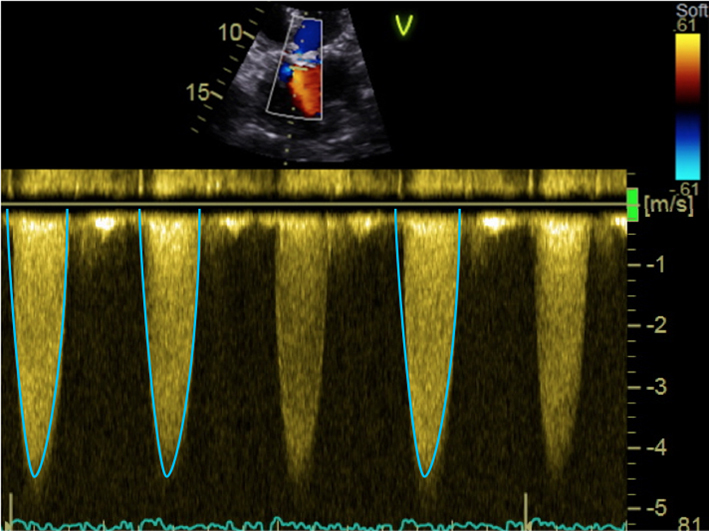 |
| Apical 5-chamber view; 2D imaging zoom | PW Doppler tracing in LVOT for calculation of stroke volume and AVA | Sweep speed 50–100 mm/s Trace around modal velocity Average three tracings in SR See ‘Essential parameters in the echocardiographic assessment of AS severity’ section for optimization and troubleshooting | 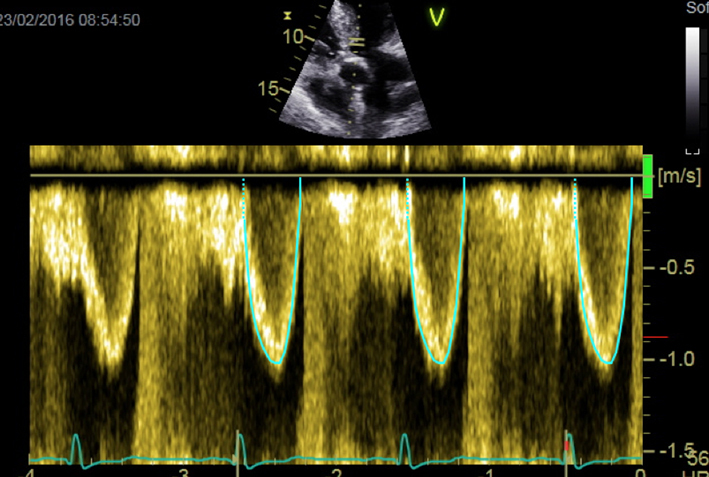 |
| Apical 2-chamber view; 2D imaging focus on LV | LV volumes and LVEF using quantitative methodology Consider assessment of GLS | LVEF is a prognostic marker in AS (see ‘Additional prognostic markers’ section) GLS is a potential marker of prognosis in AS (see ‘Additional prognostic markers’ section) | 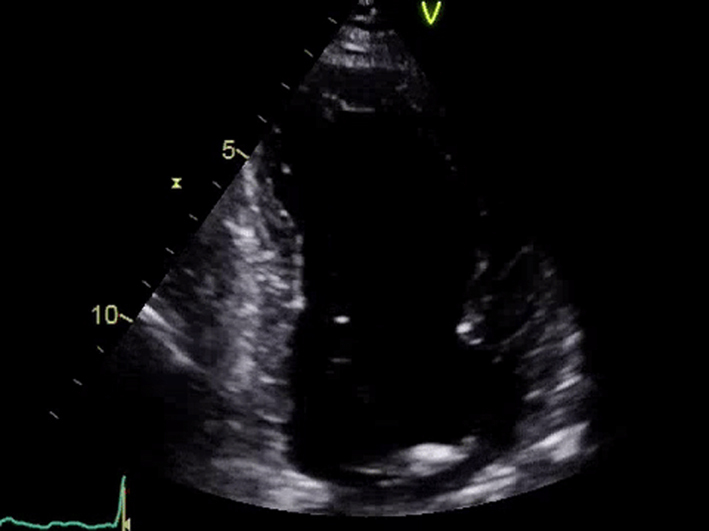 |
| Apical 3-chamber window; 2D imaging (+ colour Doppler) | Overview Calcification and mobility of aortic valve + colour Doppler for assessment of AR Consider GLS (see ‘Additional prognostic markers’ section) | 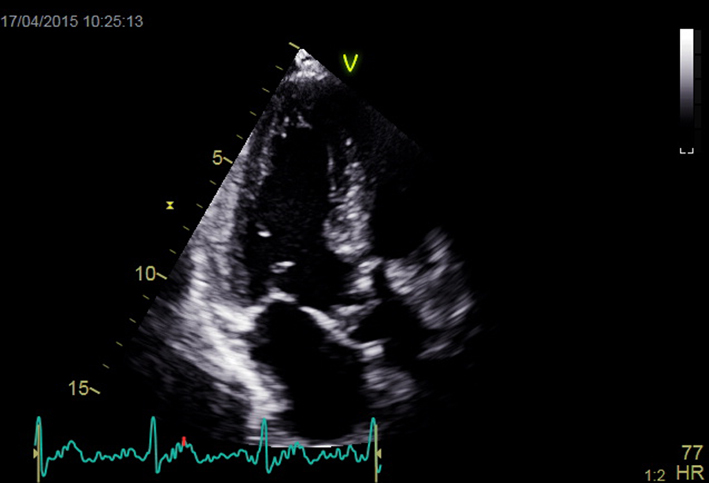 |
|
| Apical 3-chamber view; 2D imaging zoom AV + repeat CW and PW Doppler | Mobility and calcification of valve Repeat Doppler tracings for assessment of severity | 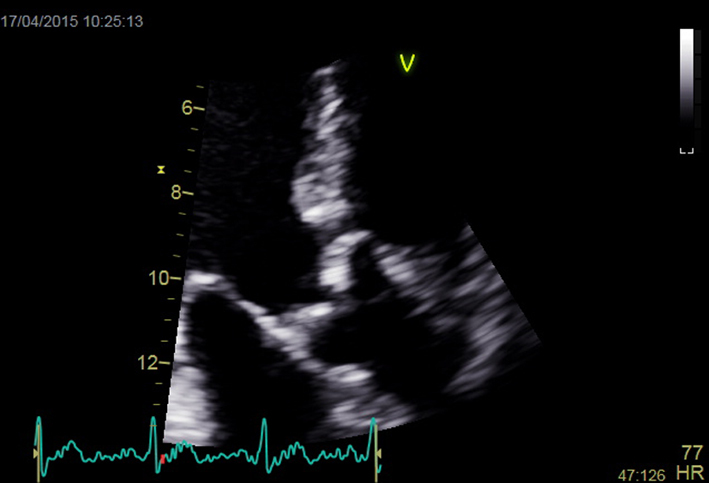 |
|
| Suprasternal notch; 2D + colour Doppler | Aortic arch | Look for turbulence and aortic pathology Repeat CW Doppler for AV Vmax and mean AVG (see ‘Essential parameters in the echocardiographic assessment of AS severity’ section) | 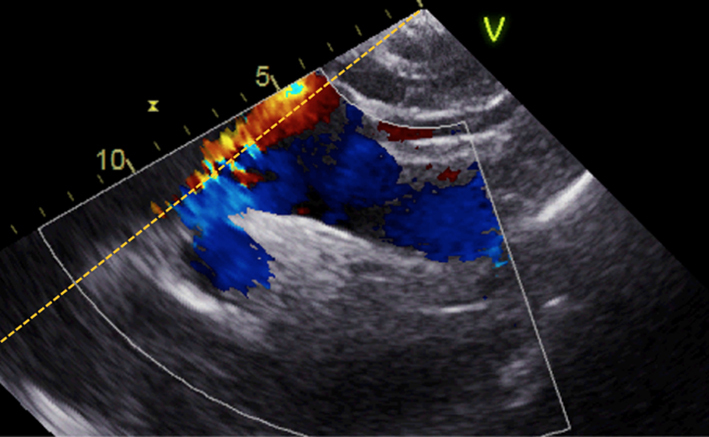 |
| Suprasternal notch; 2D + colour Doppler | Distal arch/descending aorta; look for turbulence and pathology including coarctation | 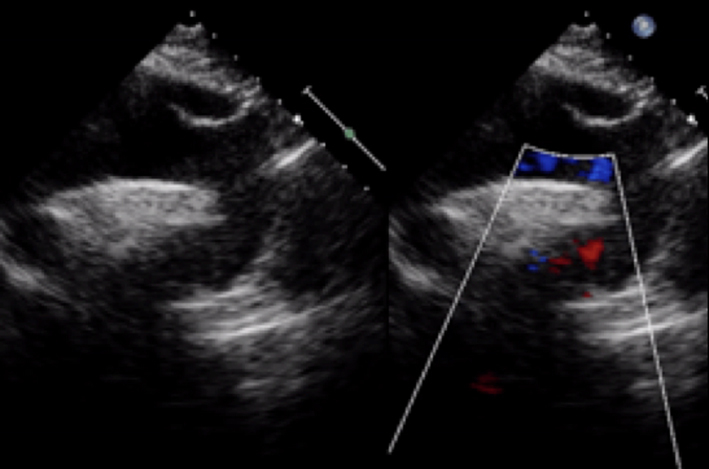 |
|
| PEDOF or standalone imaging Try all imaging windows including right parasternal (shown) | AV Vmax and mean gradient | Repeat from all imaging windows to ensure maximal values of Vmax and mean gradient are obtained | 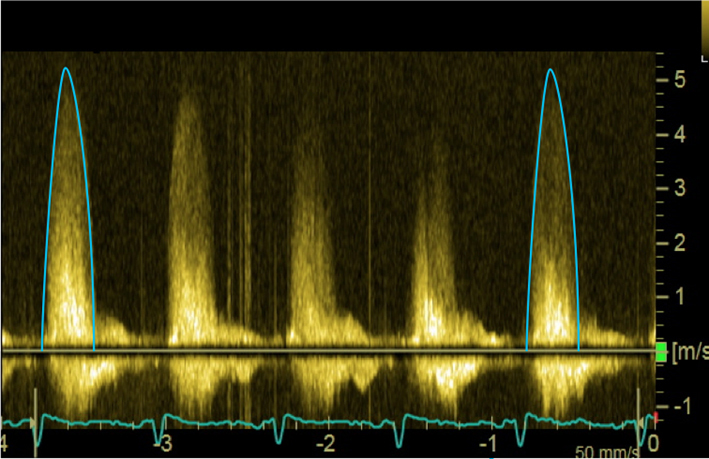 |

 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a