Figure 4.
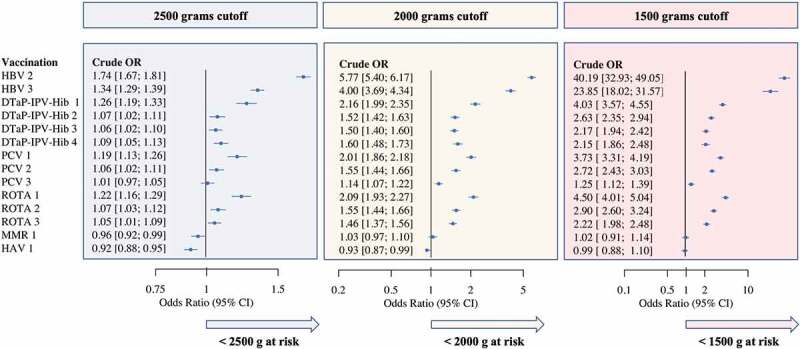
Forest plot presenting OR for risk of vaccination delay among NBW and LBW infants
Note: In early infancy LBW children are at a higher risk of vaccination delay (vaccine dose administered more than 30 d after required age), compared to NBW weight. The risk for later doses within each series is generally lower as doses progress. In some cases, vaccinations administered at older ages and not limited by earlier doses from a series show an advantage among LBW infants. Abbreviations: NBW, normal birthweight (≥2500 g); LBW, low birthweight (<2500 g).
