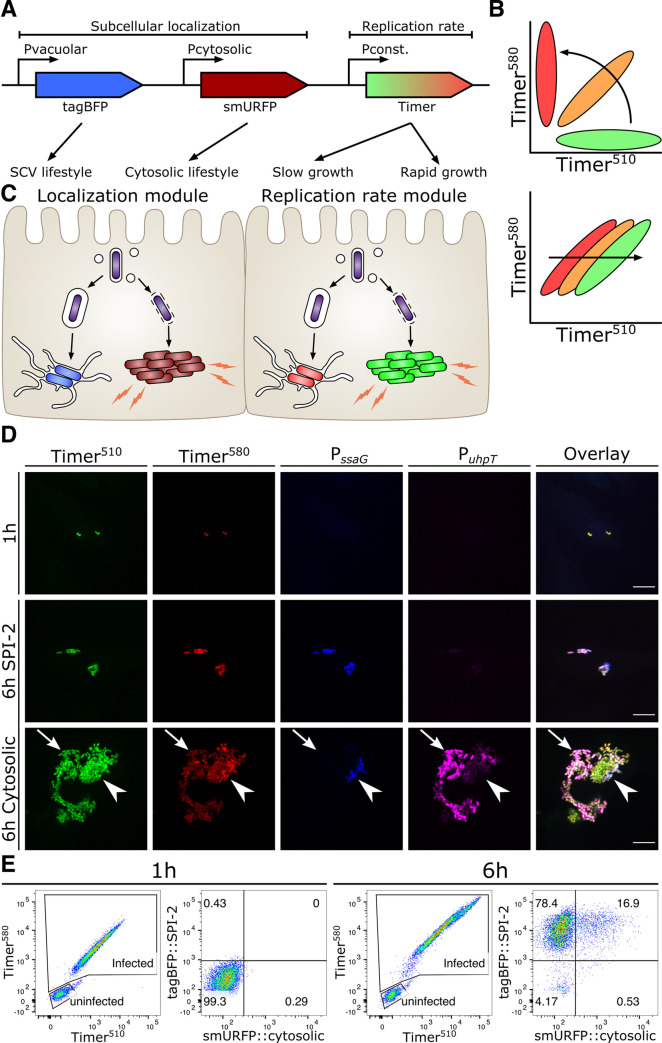
Fig 1. SINA enables precise determination of the different Salmonella intracellular lifestyles in human epithelial cells.
(A) Schematic diagram of the construction of subcellular localization and replication rate modules of SINA1.1. The subcellular localization module is composed of the vacuolar submodule (PssaG-tagBFP) and cytosolic submodule (PuhpT-smURFP), while the replication rate module is composed of a constitutively expressed Timerbac (PybaJ-Timerbac) (B) (Top) Schematic diagram of the emission spectrum shifts of S. Typhimurium harboring Timerbac as Timerbac matures, where emission shifts from green to red (Bottom) Green:Red ratio increases with elevating S. Typhimurium replication rates. As S. Typhimurium divides, both Timer510 and Timer580 fluorophores are diluted. With a higher production rate of Timer510 than Timer580, fast dividing S. Typhimurium exhibits a higher Green:Red ratio. (C) Expected output by SINA as S. Typhimurium dwells in distinct subcellular localizations. Vacuolar S. Typhimurium are of lower replication rate (i.e. lower Green:Red ratio) and are expected to emit blue fluorescence; cytosolic S. Typhimurium are of higher replication rate (i.e. higher Green:Red ratio) and are expected to emit far red fluorescence (D) HeLa cells infected by S. Typhimurium harboring SINA1.1. Output of SINA from intracellular S. Typhimurium was detected by fluorescence microscopy at 1 h pi, vacuolar (arrowhead) and cytosolic (arrow) S. Typhimurium at 6 h pi. (3 independent experiments). Scale bars are 10 μm. (E) HeLa cells infected by S. Typhimurium harboring SINA1.1. Output of SINA from intracellular S. Typhimurium at 1 h and 6 h pi was detected by flow cytometry (3 independent experiments).