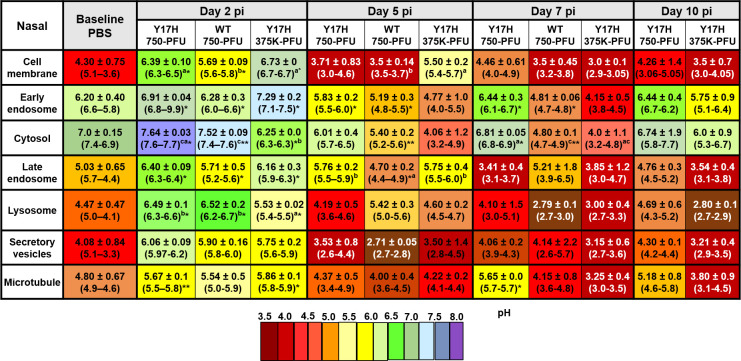
Fig 6. Intracellular pH values of uninfected (PBS) and infected live epithelial cells isolated from the nasal tissues of DBA/2J mice.
Mice were intranasally inoculated with PBS, WT virus (750 PFU), or Y17H virus (750 or 375,000 PFU). After 2, 5, 7, or 10 days of infection, following the previously reported extracellular pH measurements, single epithelial cells from a homogenate of three mice per group were isolated and analyzed with high-throughput flow cytometric analyses. A panel of the following pH dyes with different wavelengths included Oregon Green DHPE for phospholipid cell membrane pH, pHrodo Red succinimidyle (NHW) ester conjugated with an EE1 antibody as a marker of early endosomes; pHrodo Red AM for cytosolic pH; pHrodo Green STP ester conjugated with RAB7 as a marker of late endosomes; and LysoSensor Blue as a marker of lysozomes. A pHrodo Red succinimidyle (NHW) ester conjugated with a GRP94 monoclonal antibody was used as a marker of the secretory vesicles. Paclitaxel Oregon Green 488 was used as a pH marker of microtubules. Values are mean (±SD) and ranges of the homogenates of three mice from two indepenant experiments. Data were calculated from a linear standard curve generated from an intracellular pH calibration kits for each probe with Graph Pad Prism 7 (GraphPad). After calculating all fitted data, two way-ANOVA and Tukey posthoc tests for two independent experiments were performed separately for each time point. Statistically significant differences for virus-infected groups compared to the PBS group are indicated as follows: *P < 0.5, ***P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001. At each time point, statistically significant differences between the three virus-infected groups are denoted by having a different lower-case letter (a, b, or c) superscript (P = 0.001). Values with the same lower-case letters indicate no significant statistical difference between those groups.