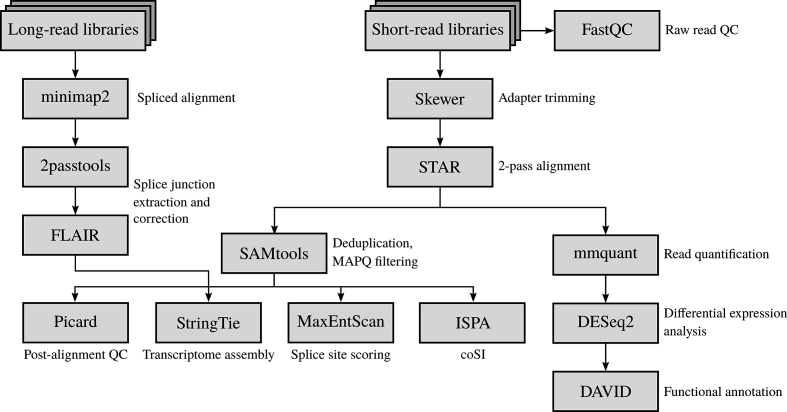
Fig. 1.
RNA-seq analysis of the HBV and host transcriptomes. QC checking of the paired-end RNA-seq libraries was carried out using fastqc. Adapter sequences were trimmed from the RNA-seq reads using skewer. Trimmed reads were aligned to the human genome and HBV pgRNAs using star in 2-pass mode. Duplicated and multi-mapped reads were discarded from the binary alignment map (BAM) files using samtools. A post-alignment QC check was performed using picard tools. PacBio CCS reads were aligned to the HBV pgRNA using minimap2. HBV splice junctions were extracted and corrected using 2passtools and flair, respectively. Reference-based transcriptome assembly and quantification were carried out using stringtie, with a post-processing step focusing on the HBV spliced transcript isoforms. Splice site sequence contexts were scored using maxentscan. Completeness of RNA splicing was evaluated using ipsa. Reads mapped to human genes were quantified using mmquant, followed by differential gene expression analysis using deseq2. A list of differentially expressed genes was submitted to the david webserver for functional annotation analysis.