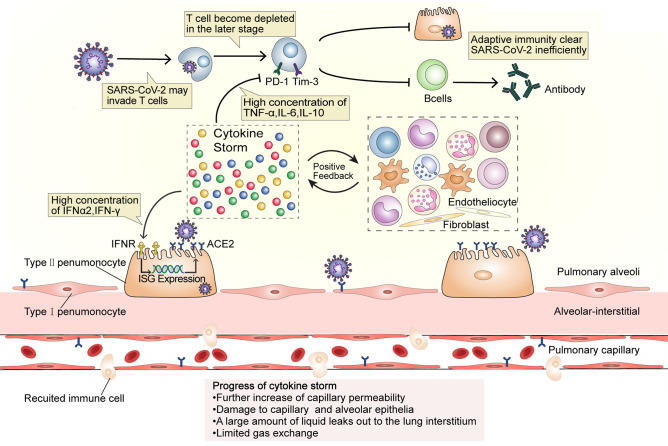
Figure 2.
A dysfunctional immune response induces cytokine storms. SARS-CoV-2 may invade T cells that are attracted to the site of infection and replicates inside them. At the later stage of COVID-19, T cells become depleted and the expression of PD-1 and Tim-3 increases, while the high IL-10, TNF, and IL-6 concentration affect T cell survival or proliferation. The number of B cells also decreases in patients with severe disease. The dysfunction of adaptive immunity results in the magnification of innate immunity and establishes an inflammatory feedback loop. High concentrations of IFN-α2 and IFN-γ may upregulate the expression of ACE2 during the cytokine storm. Additionally, as ACE2 is an ISG, its internalization will further induce ACE2 expression and eventually provide more receptors for virus invasion and aggravate the infection, thus intensify the inflammation. In this stage, capillary permeability is further increased and the capillary and alveolar epithelia become damaged, causing the leakage of a large amount of protein-rich liquid into the lung interstitium and limiting gas exchange. ISG, interferon-stimulating gene.