Fig. 5. Mical and Myo15 regulate synaptic structure and F-actin muscle organization.
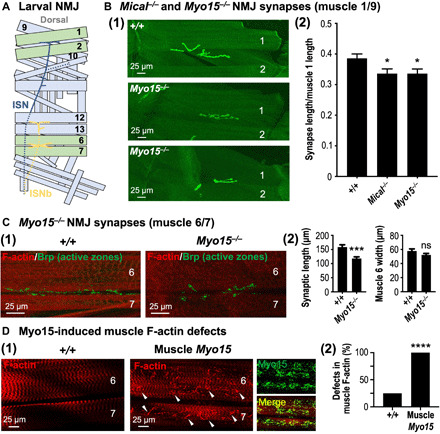
(A) Illustrated hemisegment showing the stereotypical synaptic innervation of intersegmental nerve (ISN) (blue) and ISNb (yellow) motor axons. Muscles 1, 2, 6, and 7, green; other muscles, light blue; dashed lines, nerve lying underneath/lateral to muscles. (B) Myo15−/− mutants, similar to Mical−/− mutants, have reduced synaptic innervation. Synapses visualized with CD8-GFP-Shaker (shGFP7A) (7, 45). (1) Compared to wild-type (shGFP7A/shGFP7A) synapses, which spread out along muscles 1 and 9 (top), Myo15−/− mutant synapses (Myo1521J/Y; shGFP7A/shGFP7A) are shorter (middle and bottom). Muscle 2 indicated for reference. (2) Both Mical−/− and Myo15−/− mutants have reduced synaptic innervation. Mical−/− (MicalI666, shGFP7A/MicalG56, shGFP7A). Means ± SEM. n ≥ 20 synapses/muscles (10 animals) per genotype. *P = 0.0243 (Myo15−/−) and *P = 0.0219 (Mical−/−), unpaired t test (two-tailed). (C) Synaptic innervation of muscles 6 and 7 is also shorter in Myo15−/− (Myo1521J/Y) mutants. Synapses/presynaptic active zones visualized with nc82 [Bruchpilot (Brp)] antibody. Muscles visualized with fluorophore-conjugated phalloidin. Means ± SEM. n ≥ 17 synapses/muscles (10 animals) per genotype. ***P = 0.0002 and ns, P = 0.1395, unpaired t test (two-tailed). (D) Elevating Myo15 in muscles (Muscle Myo15 = UAS:Myo15GFP/+, 24B-GAL4/+) significantly alters F-actin (red) organization [(1) and (2)], including disrupting its striated pattern (1) and inducing clumping (arrowheads). Myo15 (green) localizes with these F-actin defects (merge). n ≥ 19 synapses/muscles (10 animals) per genotype. ****P < 0.0001, chi-square test.
