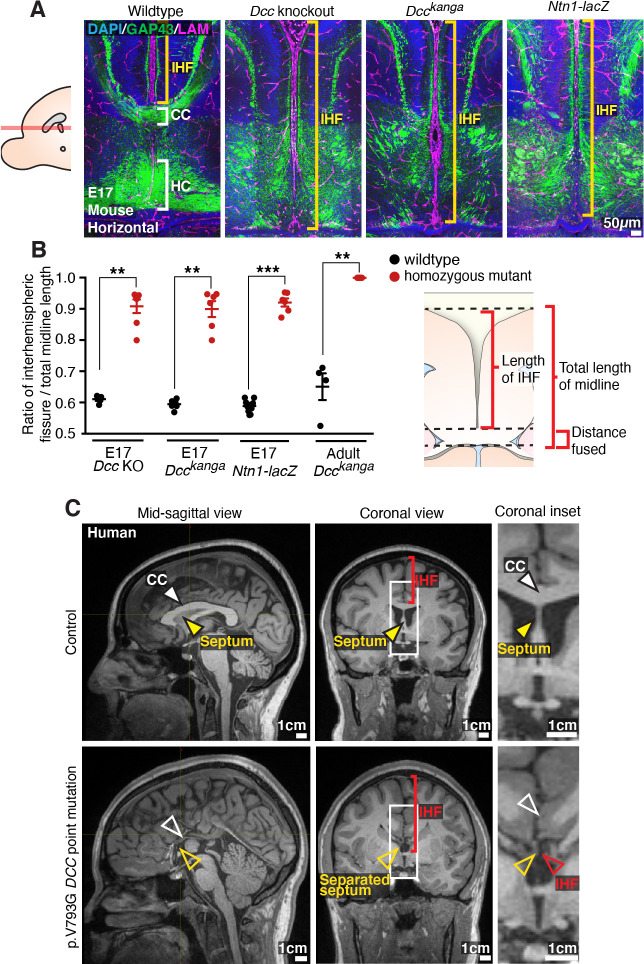
Figure 1. Netrin 1 (NTN1) and deleted in colorectal carcinoma (DCC) are crucial for remodelling of the interhemispheric fissure (IHF), corpus callosum (CC) and hippocampal commissure (HC) formation.
(A) Staining for Gap43-positive axons (green) and pan-Laminin (LAM)-positive leptomeninges and basement membrane (magenta) in wildtype, Dcc knockout, Dcckanga, and Ntn1-lacZ mice at embryonic day (E)17 indicates midline formation or absence of the CC and HC (white brackets) and extent of the IHF (yellow brackets). (B) The ratio of IHF length over the total midline length with schema. (C) T1-weighted MR images of a control subject compared with an individual with a DCC mutation demonstrate the presence or absence of the CC (white arrowheads) and extent of the IHF (red arrowheads and brackets) within the septum (yellow arrowheads). Graph represents mean ± SEM. Statistics by Mann–Whitney test: **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. See related Figure 1—figure supplement 1 and Supplementary file 1.
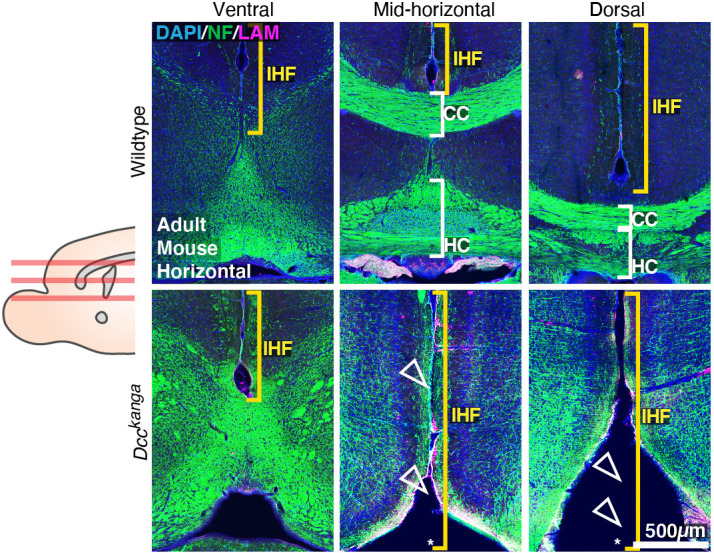
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. The interhemispheric fissure (IHF) is not remodelled in adult Dcckanga mice.