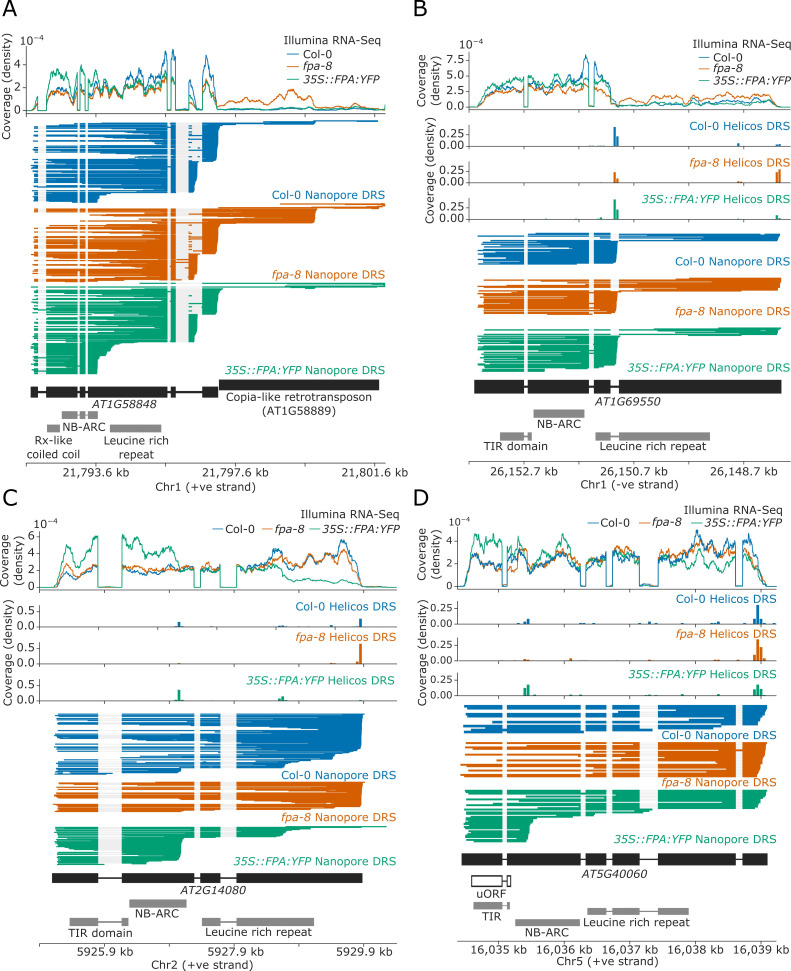
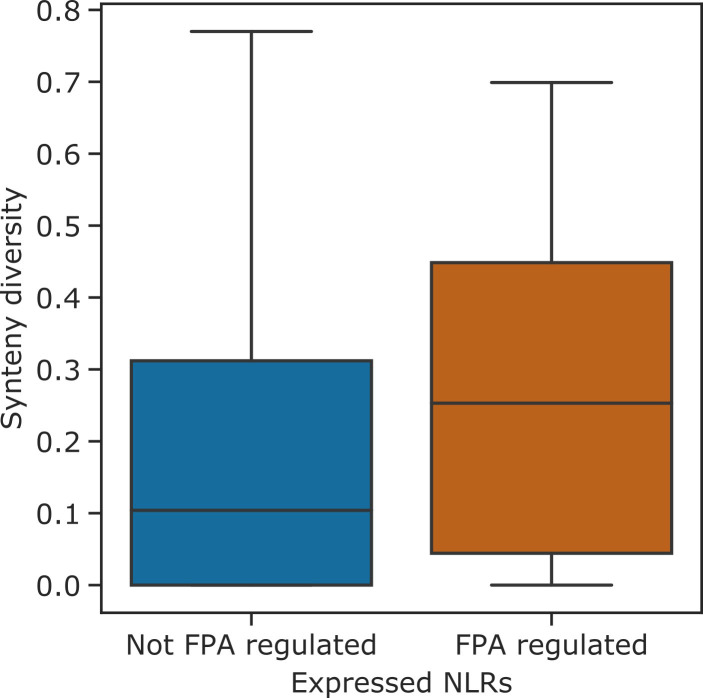
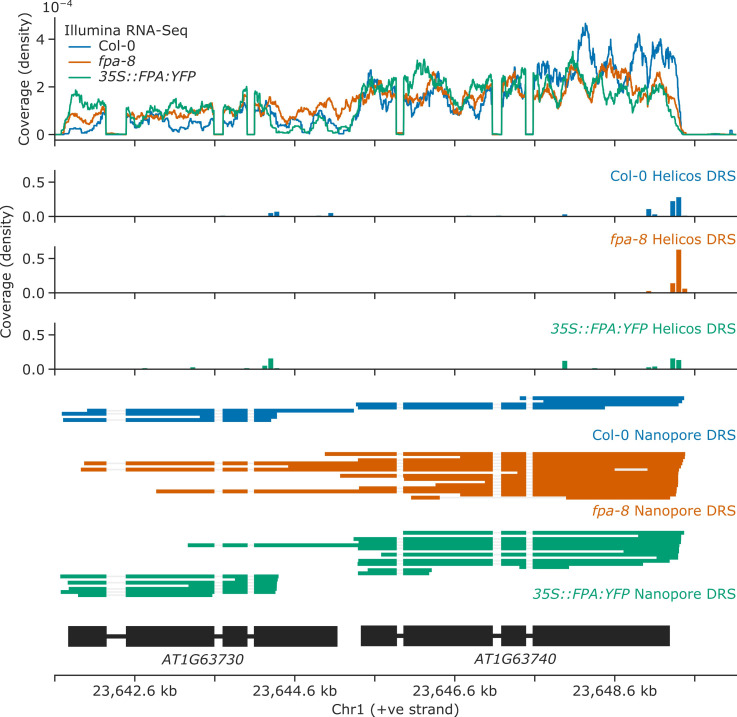
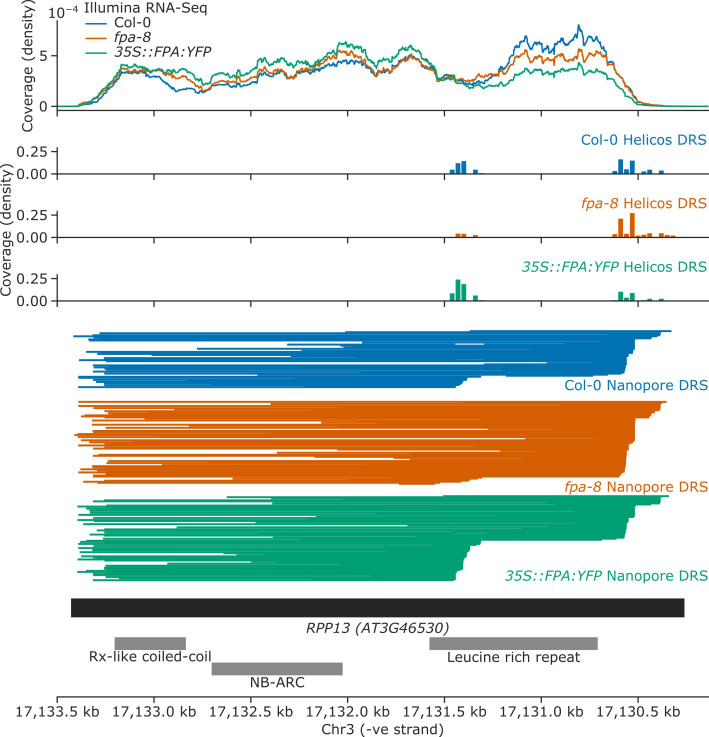
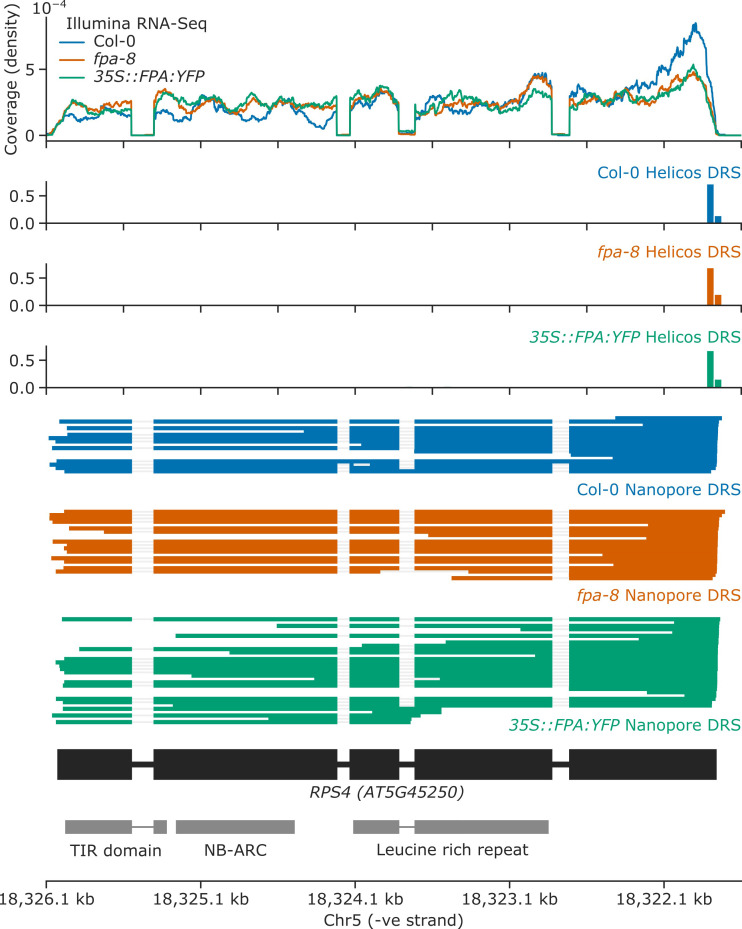
Figure 4. FPA-dependent alternative polyadenylation of NLR transcripts.
FPA controls (A) readthrough and chimeric RNA formation at AT1G58848 (unique mapping of short Helicos DRS reads was not possible due to the high homology of AT1G58848 to tandemly duplicated NLR loci in the same cluster); (B) intronic polyadenylation at AT1G69550, resulting in transcripts encoding a protein with a truncated LRR domain; (C) exonic polyadenylation at AT2G14080, resulting in stop-codonless transcripts; and (D) exonic polyadenylation at AT5G40060, resulting in transcripts encoding a TIR-domain-only protein due to an upstream ORF.