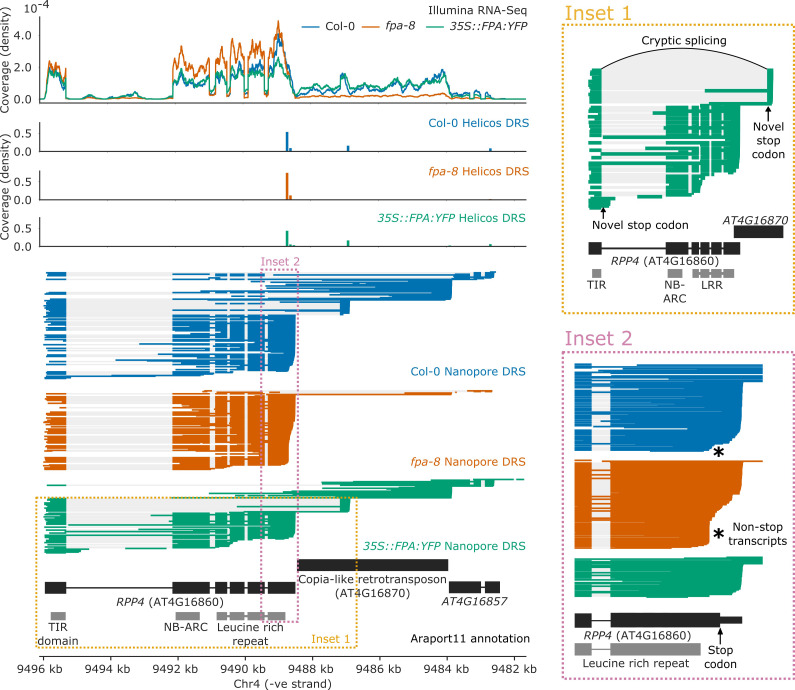
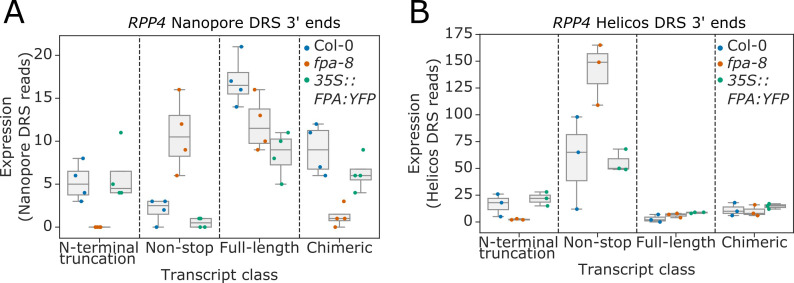
Figure 5. Complex FPA-dependent patterns of alternative polyadenylation at RPP4.
FPA-dependent intronic, exonic and readthrough poly(A) site selection in RPP4. (Inset 1) A magnified view of TIR-domain-only RPP4 transcripts detected in 35S::FPA:YFP caused by proximal polyadenylation in intron 1, and distal polyadenylation within the TE associated with cryptic splicing. (Inset 2) A magnified view of the stop-codonless transcripts produced within the protein-coding RPP4 region in fpa-8.