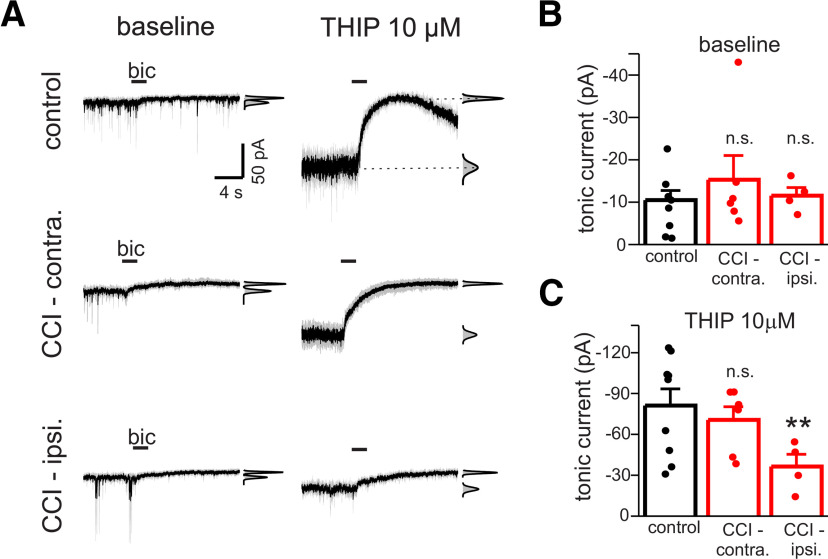
Figure 2.
CCI reduces THIP-induced tonic currents, but not basal tonic currents, in ipsilateral DGGCs. A, Membrane currents of DGGCs in response to focal application of the GABAA receptor antagonist bicuculline (Bic) application before and during exposure to THIP (10 μm). CCI data recorded two weeks after injury. Illustrated currents are mean response (black line) of three focal applications of Bic overlaid with the individual responses to Bic in each cell (gray line). Insets to right of each trace represent all-points histogram and Gaussian fits used to measure mean holding current before and after Bic application; tonic current amplitude is defined as difference in mean holding current produced by Bic. Horizontal bars represent period of drug application in this and subsequent figures. Holding potential was −70 mV. B, Mean baseline tonic current (±SEM) of DGGCs in control, CCI-contra, or CCI-ipsi slices. Baseline tonic currents were unaffected by CCI two weeks after injury. Solid circles represent data from individual cells in this and subsequent figures. C, Mean THIP-induced tonic current of DGGCs in control, CCI-contra, or CCI-ipsi slices. CCI significantly reduced amplitude of THIP-induced currents in CCI-ipsi cells only; **p < 0.01, n.s., not significant.