Figure 7.
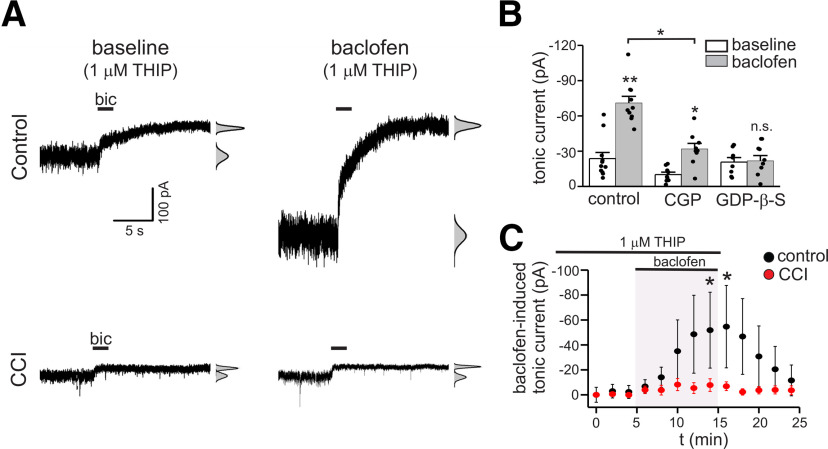
Enhancement of tonic currents by postsynaptic GABAB receptors is attenuated after CCI. A, Membrane currents in response to bicuculline (bic) application in control and CCI-ipsi cells before (left panel traces) and during baclofen (10 μm) application (right-panel traces). All data in this figure were recorded in the presence of low concentrations of THIP (1 μm). B, Mean tonic current at baseline and during baclofen application for cells studied under control conditions, with the GABAB receptor antagonist CGP (10 μm), or with intracellular GDP-β-S (0.5 mm). Baclofen significantly increased tonic currents under control conditions. This effect was partially blocked by CGP, with significant reduction in magnitude of tonic current change compared with control. Disruption of G-protein signaling with intracellular GDP-β-S prevented baclofen-induced tonic current increases. C, Time course of tonic current change during baclofen application (baclofen-induced tonic current) in control and CCI-ipsi cells; n.s., not significant. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.