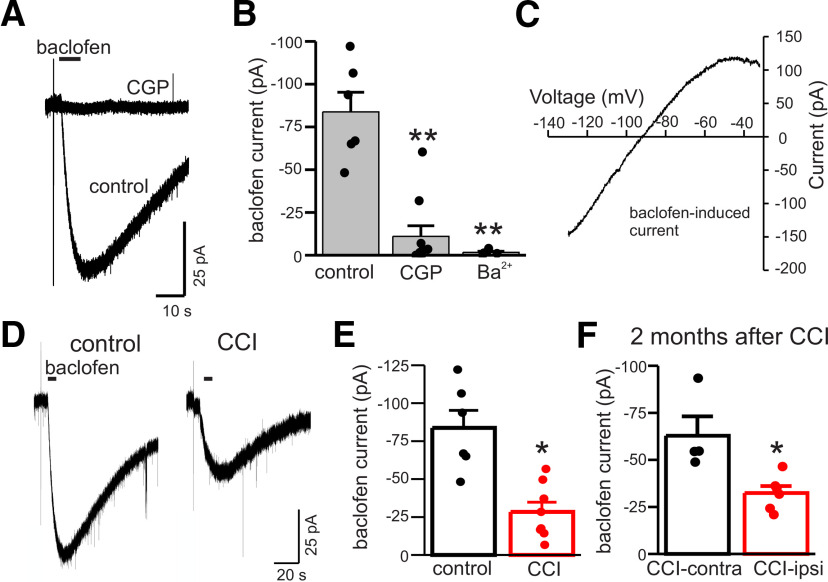
Figure 8.
CCI reduces GABAB receptor activated K+ currents. A, Membrane currents in response to focal application of baclofen (100 μm, 5-s application) before and during bath application of CGP (10 μm). Currents were measured with K+-gluconate pipette solution at −110 mV. B, Mean current induced by baclofen under control conditions, with GGP, or the K+ channel blocker Ba2+ (100 μm). CGP and Ba2+ inhibited baclofen-induced currents by 74% and 82%, respectively. C, Current-voltage plot of ramp current induced by baclofen (subtracted). Baclofen-induced ramp currents were inwardly-rectifying and the illustrated current reversed direction at −90 mV. D, Baclofen-evoked K+ currents in control and CCI-ipsi DGGCs. E, Mean GABAB receptor activated K+ current in control and CCI-ipsi cells. On average, CCI reduced GABAB receptor-activated K+ currents by 66%. F, Mean GABAB receptor activated K+ current in CCI-contra and CCI-ipsi DGGCs two months after CCI. GABAB receptor activated K+ currents are reduced in CCI-ipsi cells by 48% compared with CCI-contra cells two months after injury. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.