Figure 2.
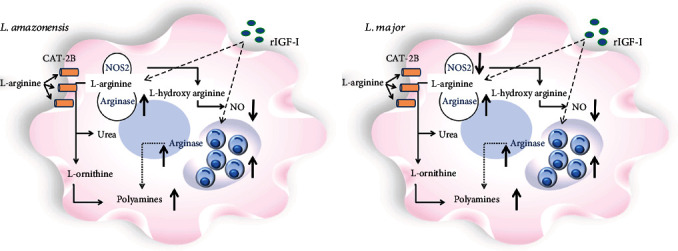
Scheme of the effect of extrinsic IGF-I (rIGF-I) in the L-arginine metabolic pathway activation in macrophages infected by L. amazonensis and L. major. In RAW 264.7 cells or BALB/c mouse peritoneal macrophages infected with L. amazonensis or L. major promastigotes and stimulated with 50 ng/mL recombinant IGF-I (rIGF-I, R&D Systems, USA), the parasitism, arginase mRNA expression, and arginase activity, nitric oxide synthase 2 (NOS2) mRNA expression, and nitric oxide production (Griess reaction) were evaluated. Extrinsic IGF-I induced an increase in arginase expression and arginase activity in both parasites and macrophages, decreased the production of NO, and increased the parasitism in L. amazonensis- and L. major-infected cells, comparably.
